Dural Sac: Anatomy, Roles And Pathologies
Di: Ava
What is a Thecal Sac : Definition and Structure The thecal sac is a covering of the spinal canal that is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It houses the spinal cord and nerve roots. It is made up of outer arachnoid membrane and inner dura. It is wider in females. The length is approximately until S1 to S3 vertebral levels. It elongates and moves upwards upon spinal The spinal cord thins from a cranial to caudal direction, with the cord terminating in adults at L1/2 and the dural sac at S2. 1 The epidural space is bounded by the bony structures of the spinal column, excludes the contents of the dura, and communicates with the paravertebral spaces via the spinal foramina, from which nerve roots The dural is a vital component of the human spinal cord. Understanding its structure and function is crucial for maintaining spinal health.
Recent research on the ultrastructure of the human spinal dural sac and its contents has enhanced our understanding of the microstructure of the
Three-dimensional visualization of internal/external VVP (blue) and dural sac (d posterior view; e anterior view). Although these images include both veins and arteries, we can identify the vein diacritically by its shape Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a surgical emergency caused by compression of the lower spine’s thecal sac.
Anatomy and Clinical Importance of the Epidural Space
Pathologies affecting the spinal epidural space (SES) comprise various abnormalities. However, they all have the potential to cause thecal sac narrowing or spinal cord compression. In this review, we group these pathologies into degenerative, infective, neoplastic, vascular, traumatic, and others, focusing on their imaging features. Degenerative pathologies
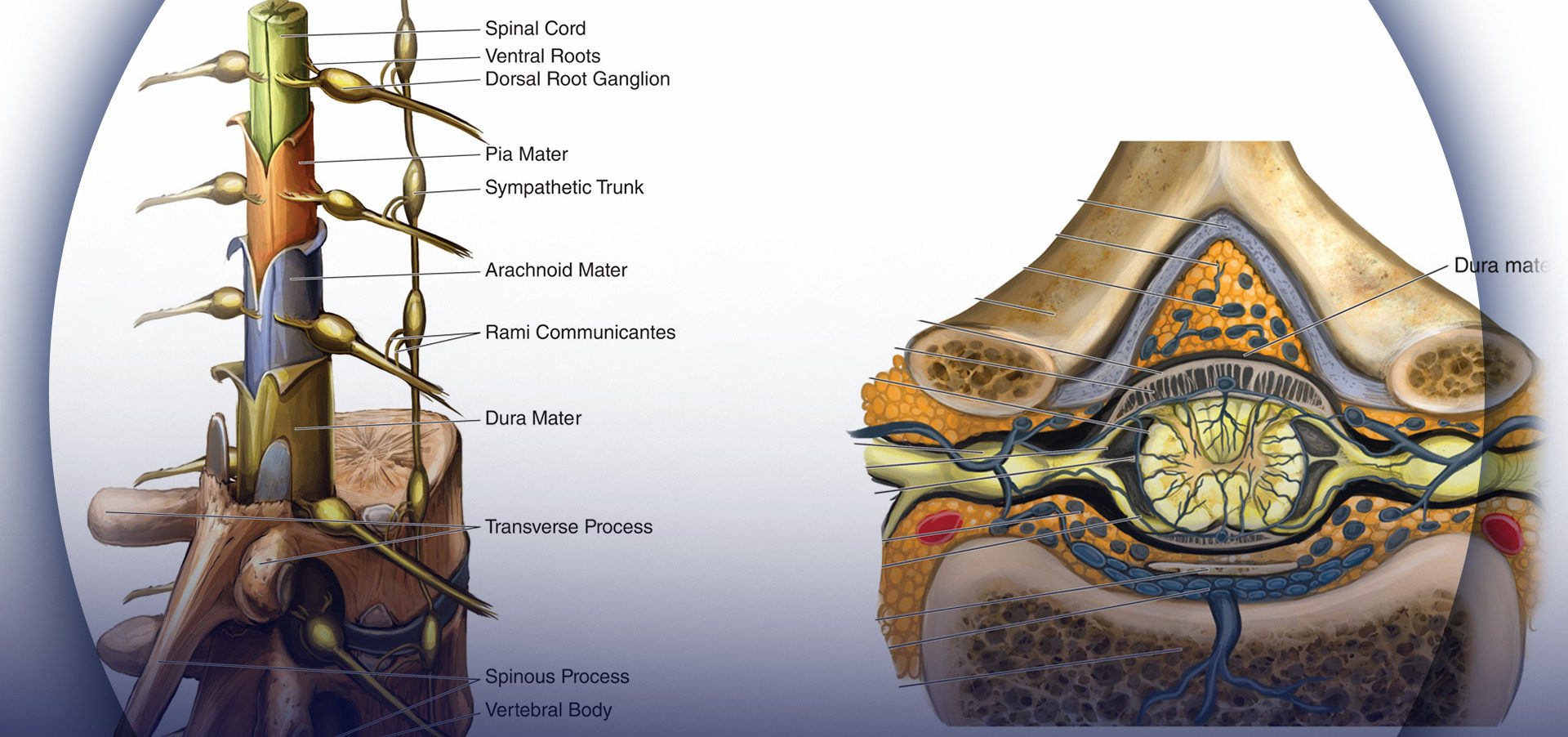
The dural sac generally ends at the lower border of S2 below which it continues as the filum terminale, a structure clearly and frequently seen with spinal endoscopy. The dural sac contains the anterior and posterior spinal nerve roots, collectively know as the cauda equina. The thecal sac, also known as the dural sac, is a protective membrane that surrounds the spinal cord and contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Here’s a detailed look at its anatomy and applied
Key Features/Anatomical Relations The spinal dura mater forms the dural sac, running from the foramen magnum rostrally to the S2 vertebrae caudally. The spinal dura extends laterally with nerve roots to cover nerves as they emerge from the spinal canal. The dura mater blends with the epineurium of the spinal nerves. The wide availability of ultrasound, along with its lack of ionizing radiation burden and need for sedation for most exams, often make sonography the first line in the imaging evaluation of children. The developing osseous anatomy of the spine in young infants provides a distinct window allowing for a detailed depiction of the spinal canal and its contents, which is
- Conus and Cauda Equina Tumors
- Spinal Stenosis: Practice Essentials, Anatomy, Pathophysiology
- Nerves of the lumbar spine
- Journal of Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery and Technique
- Dural and Leptomeningeal Diseases: Anatomy, Causes, and
Download scientific diagram | Determination of the lumbosacral dural sac termination levels. On magnified midsagittal CT myelogram images of the distal spine, we recorded the level of termination Conjoined nerve roots are a type of nerve root anomaly described in human medicine and are defined as two nerve roots that either share a common dural envelope at some point during their course from the dural sac or that have Dural Sac is often injured while epidural injections or spinal surgery that causes cerebral spinal fluid leaks. Chronic severe headaches along with dizziness, among other concerns are among the symptoms. The dural sac is occupied by cerebral spinal fluid and in MRI imaging reports for back pain, it is often included notably.
Dural and Leptomeningeal Diseases: Anatomy, Causes, and
Narrowing of the dural sac cross-sectional area (DSCSA) and spinal canal cross-sectional area (SCCSA) have been considered major causes of lumbar central canal spinal stenosis (LCCSS). DSCSA and SCCSA were previously correlated with subjective Știi expresia „sac dural“? Cu siguranță nu. Oamenii tind să fie interesați de ceva numai în cazul în care le privește. Dar, probabil, este mai bine să știi unele lucruri în avans, ceea ce apoi, dacă ceva, se confruntă cu o masă de expresii necunoscute. sacul dural și totul despre el În primul rând trebuie să spunem ceea ce va ajuta la cunoașterea termenului. Dural sac
Diagnosis of extramedullary spinal diseases is often complex, firstly requiring a good anatomic knowledge for a precise localization of pathologies. The spinal canal, a tubular space delimited by vertebral bodies and neural arches, contains the spinal cord, nerve roots and cauda equina. Neural structures are surrounded and supported, from outer to inner, by
A broad spectrum of spinal pathologies can affect the pediatric population. Ultrasound (US) is the primary modality for pediatric spine assessment due to its widespread availability, non-requirement of sedation, and absence of ionizing radiation. Rôle neurologique du rachis lombaire La moelle épinière s’arrête entre L1 et L2 ensuite on a la queue de cheval et les racines. Il est important de bien This study demonstrated the anatomy of the nerve roots, rootlets, and intervertebral foramina, and may aid in understanding the pathology of cervical radiculopathy. The presence of intradural connections between dorsal nerve roots and the relation between the course of the nerve root and the interve
In this pictorial essay, detailed anatomy of the posterior epidural space, pathologies affecting it along with imaging pearls to accurately diagnose them are discussed. Various pathologies affecting the posterior epidural space either arising from the space itself or occurring secondary to vertebral/intervertebral disc pathologies. The spinal meninges (singular: meninx) are contained within the spinal canal and encase the spinal cord, spinal nerve roots and the cauda equina. Gross anatomy They are composed of three layers (outer to inner) dura mater (also known as t filum terminale residual fragment of spinal cord that extends from the conus medullaris to the sacrum thecal sac dura-surrounded sac that extends from the spinal cord and contains cerebrospinal fluid, nerve roots, and the cauda equina cauda equina nerve roots and filum terminale that extend from the spinal cord and are surrounded by dura
Conus and cauda equina tumors represent a unique group of tumors due to their specific location in the spinal canal. The conus medullaris forms the last portion of the spinal cord from where the axons of the distal nerve roots originate and where the spinal bowel and bladder centers are located. The cauda equina is the conglomeration of the nerve roots of the lumbar Epidural fat This is the fat that surrounds the dural sac, that contains the nerves. Abundant fat can be seen in steroid therapy, extreme obesitas and rarely idiopathic. Abundant epidural fat can contribute to stenosis of the spinal canal. The dural sac is continuous with the foramen magnum, extending to the lower border of S2, where it spreads distally to cover the filum terminale. The spinal nerves emerging from the cord form the peripheral nervous system.
Imaging review of the atypical spinal epidural space pathologies
A sound knowledge of applied anatomy is the cornerstone of safe and effective regional anaesthesia. In this update we revise the anatomy of the epidural space and relevant adjacent anatomy, using bespoke anatomical dissections, to enable the reader to form a 3-dimensional picture to assist their clinical practice. Sonoanatomy, common techniques for locating the INTRODUCTION Several reports of dural sac (DS) termination anatomy using magnetic resonance imaging and cadaver examinations have been published to date, and it is generally accepted that the mean level of DS termination lies at the second sacral vertebrae [1, 6, 11, 12]. Spine surgeons are not often interested in the location of DS termination, but radiotherapists
Meningeal lesions can be caused by various conditions and pose diagnostic challenges. The authors review the anatomy of the meninges in the brain and spinal cord to provide a better understanding of the localization and extension of these diseases and summarize the clinical and imaging features of various conditions that cause dural and/or leptomeningeal However, because vascular lesions in this region are infrequent, and the anatomy is unique, understanding the pathology is not always easy. Therefore, in this era of improved magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography (MRI/MRA) quality and high resolution spinal angiography, accurate knowledge of the vascular anatomy in the cauda Afecțiunile sacului dural, precum compresiile, rupturile sau scurgerile de lichid cefalorahidian, pot provoca simptome neurologice semnificative, inclusiv dureri, slăbiciune musculară sau disfuncții ale vezicii urinare. Diagnosticarea precisă a problemelor sacului dural necesită imagistică avansată precum rezonanța magnetică, iar tratamentul variază de la
Imaging of the pediatric spine differs from that in adults in terms of relevant anatomy and associated pathology. An accurate imaging evaluation requires familiarity with the wide differential diagnosis of pediatric spinal disease. Spinal stenosis results from progressive narrowing of the central spinal canal and the lateral recesses. The essential content of the spinal canal includes the spinal cord, the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the thecal sac, and the dural membranes that enclose the thecal sac.
The thecal sac or dural sac is the membranous sheath (theca) or tube of dura mater that surrounds the spinal cord and the cauda equina. The thecal sac contains the cerebrospinal fluid which provides nutrients and buoyancy to the spinal cord. [1]
- Dubrovnik Für Junge Leute Geeignet?
- Dur-Line Dcs 551-24 Sat Einkabellösung Bis 24 Teilnehmer
- Dunlop Echoplex Delay Guitar Effects Pedal
- Dulces Venezolanos De Semana Santa: Sabores De Tradición
- Dvd Scrubs Staffel 1 In Baden-Württemberg
- Dusk Till Dawn Online Poker | News: Jake Betts wins GGPoker UK Poker Championships
- Dymo Labelmanager 450 User Manual Pdf Download
- Dynamische Stabilitäts-Control; Dsc
- Dungeon Crawling Seigfried | Best Dungeons Minecraft Servers
- Duplicado Tarjet Prepago Lebara
- Dublin Third Most Expensive City In Europe For Construction Costs
- Duisburg: Das Ist Der Höchste Gipfel Der Stadt
- Dynamics And Multi-Scale Modeling With Time Delays For Three
