Does The Electron Have An Intrinsic Magnetic Moment?
Di: Ava
The quantity is a fundamental unit of magnetism called the Bohr magneton, which has the value (J/T) or Quantization of the magnetic moment is the result of quantization of the orbital angular momentum. As we will see in the next section, the total magnetic dipole moment of the hydrogen atom is due to both the orbital motion of the electron and its intrinsic spin. For now, we ignore
We know now that the electrons have always been spinning, and always have a magnetic moment. It is simply a matter of aligning these spins to produce an overall magnetic effect.
1.12: Electron spin and multi-electron atoms

Does an electron really spin about its own axis? If not, what does spin magnetic moment imply? My physics teacher said „Besides the orbital moment, an electron has an intrinsic magnetic moment, it is called the spin magnetic moment, But I hasten to add that it is not as though the electron is spinning.“ But, in my chemistry textbook, there’s an illustration of an
Magnetic moments due to movements of electrons, orbital and spin does not cancel it out in paramagnetic materials, therefore a net magnetic moment is present on each atom, mainly owing to the spin of electrons are incomplete or unpaired. From the tiny magnetic moments of electrons to the large-scale magnetization of materials, understanding magnetic moments is essential for
When you have moving electric charges, like a proton or electron, magnetic fields are produced. Properties of this field will depend on intrinsic magnetic moments of the involved particles and their spin states of the neutrons/protons/etc. (different from the resonance spinning that I think you are talking about). Why this happens is more complicated and depends on special relativity If the magnetic moment of the electron and orbital magnetic moment of the electron are antiparallel, the potential energy from the magnetic interaction is relatively high, but when these moments are parallel, the potential energy is relatively small.
- The Magnetic Moment and Spin of an Electron
- SATHEE: Physics Magnetic Moment Of Electron
- 3.10: Magnetic Behavior of Atoms, Molecules, and Materials
Magnetic moment is a measure of the strength and direction of a magnetic source, often associated with the spin and orbital motion of electrons.
Magnetic Moments The magnetic moment of an electron, measured in Bohr magneton units, is −9.2740. The Bohr magneton is defined as ½ h e/m e in the SI system and ½ h e/ (m e c) in the cgs system where e is the unit of electrical charge, h is the reduced Planck’s constant, m e is the rest mass of an electron and c is the speed of light. An intrinsic magnetic field is a magnetic field that originates from the atomic or subatomic particles themselves, particularly due to the motion of electrons and their spin. This internal source of magnetism contrasts with externally applied magnetic fields. However, it turns out that the intrinsic magnetic moment of the proton is μp = 2.79 μnucl. Moreover, the neutron, despite its electrical neutrality, has its own magnetic moment, equal to μn = −1.91 μnucl (the minus sign indicates that the direction of the spin is opposite to the direction of the magnetic moment). Such difference between the magnetic moments of nucleons and those
How does the electrons‘ intrinsic spin influence the direction of the electrons‘ movement during the alignment of the dipole moment to the external magnetic field?
Why are materials magnetic?
Quantization of the magnetic moment is the result of quantization of the orbital angular momentum. As we will see in the next section, the total magnetic dipole moment of the hydrogen atom is due to both the orbital motion of the electron and its intrinsic spin. For now, we ignore the effect of electron spin. As a result, whenever an energy level is completely filled, there is no net magnetic moment. This means that atoms that have quantum states with paired electrons have zero net magnetic moment. However, a number of metal atoms have unpaired electrons. For example, transition metals and lanthanides have unpaired d and f electrons, respectively.
The magnetic moment quantifies how an object responds to an external magnetic field or generates its magnetic field. The formula for
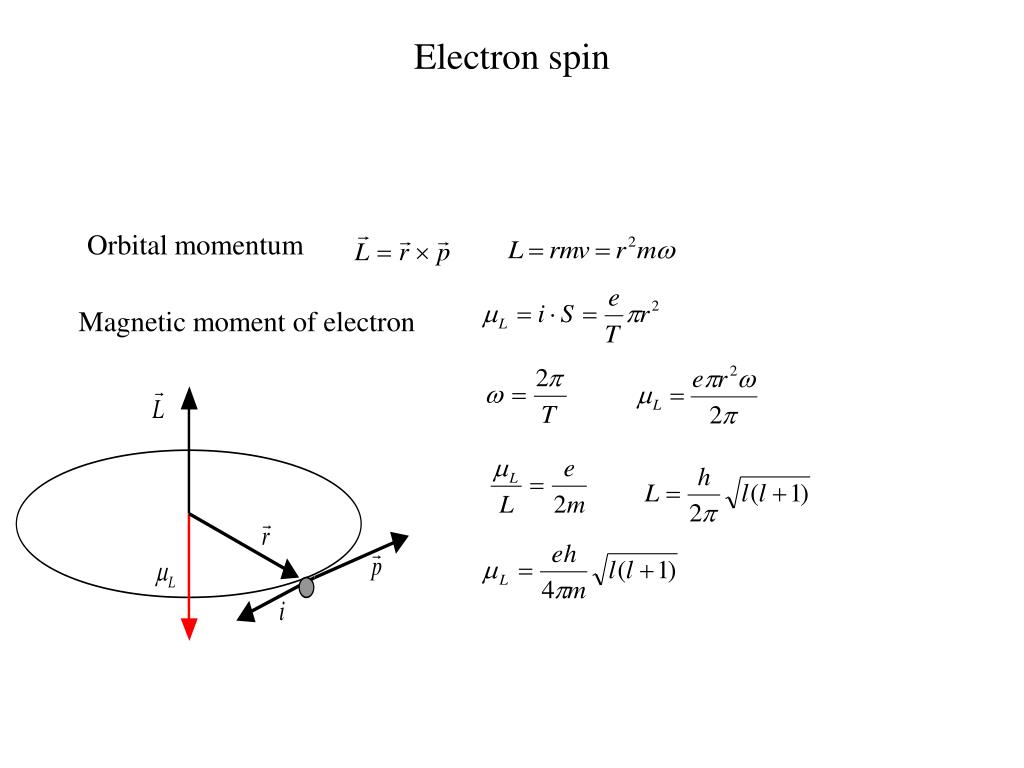
An electron is not a spinning ball of charge and the intrinsic spin of particles cannot be understood in such terms. Not only is it difficult to make sense of what it means for a pointlike particle to spin, but also when treating the electron as a spinning ball of charge one finds a value of the ratio between the magnetic moment and the angular momentum that is a factor In the previous articles on the magnetic moment, we have discussed an expression for the magnetic moment that is $ (\mu = IA)$. We have used this equation to obtain various forms of the magnetic moment. But this expression did not give a complete picture of the magnetic moment because this expression did not tell anything about the intrinsic magnetic moment of the
That is, an electron has an intrinsic magnetic moment \ (M\) arising from a degree of freedom that has no classical analog. The magnetic moment must take on only 2 values according to the Stern-Gerlach experiment. Electron Spin – hyperphysics.gsu.edu Electron spin
The intrinsic magnetic moment of an electron is equal to the magnetic moment that we obtain by effects of orbital motion of a hydrogen electron in the lowest shell (1 Bohr magneton), using classical physics. Is this merely a coincidence or is there any relation between the quantum mechanical spin moment and the classically obtained orbital moment? The existence of the neutron’s magnetic moment and the large value for the proton magnetic moment indicate that nucleons are not elementary particles. Electric and magnetic properties of electrons, as well as their electromagnetic interactions dictate many properties of matter, obviously electrical, electronic and magnetic, but also chemical properties. The small size of electrons allows obtaining much finer resolution of an electron microscope than it is possible for an optical microscope.
Magnetic Moment: Definition, Dipole & Formula
Published in: Phys.Rev. 73 (1948) 412-412DOI: 10.1103/PhysRev.73.412 Hydrogen atoms have a single electron with two spin states giving the two spots observed; silver atoms have closed shells which do not contribute to the For example, an electron possesses an intrinsic electric charge whose existence is independent of the state of the electron, or its placement inside or outside of an atom. Each electron also exhibits intrinsic spin magnetic moment. Magnetic properties of a given material can also be intrinsic or extrinsic. For example, an introduction of an air gap to a magnetic circuit changes
The spin magnetic moment is a vector quantity that represents the magnetic strength and orientation of an electron’s intrinsic angular momentum, or spin. This property arises due to the electron’s charge and its motion, influencing how it interacts with external magnetic fields. The spin magnetic moment plays a critical role in determining the behavior of current loops when
Except for its intrinsic magnetic momentum related to its spin, an electron in an atomic orbital produces a magnetic field only if it possesses an orbital angular momentum, which also produces a magnetic moment. Donate here: http://www.aklectures.com/donate.phpWebsite video link: http://www.aklectures.com/lecture/electron-spin-magnetic-dipole-momentFacebook link: htt
The electron electric dipole moment de is an intrinsic property of an electron such that the potential energy is linearly related to the strength of the electric field: U = − d e ⋅ E . {\displaystyle U=-\mathbf {d} _ {\rm {e}}\cdot \mathbf {E} .} The electron’s electric dipole moment (EDM) must be collinear with the direction of the electron’s magnetic moment (spin). [1] Within the First, in many substances the atoms have no permanent magnetic moments, or rather, all the magnets within each atom balance out so that the net moment of the atom is zero. The electron spins and orbital motions all exactly balance out, so that any particular atom has no average magnetic moment. Because the electron has an intrinsic angular momentum, we know that the electron must have an intrinsic magnetic field. Similar to a magnetic dipole field, the electron is nature’s smallest magnet.
I have read an electron has an intrinsic magnetic dipole moment. Does this mean that because dipole moment can be thought of as a current loop, and a current loop radiates EM Waves due to a changing dJ/dt d J / d t that electrons
Magnetic dipole moment of electron
Phys.Rev. 72 (1947) 241-243, Selected Papers on Quantum Electrodynamics, Edited by Julian Schwinger, New York: Dover Publications 1958 (p136-138) All electrons have intrinsic magnetic moments, whether they are moving along a wire or not so no, they are not the same thing/ effect, to sum your questions above.
In atomic physics, the electron magnetic moment, or more specifically the electron magnetic dipole moment, is the magnetic moment of an electron caused by its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. The electron magnetic moment has recently been measured to an accuracy of 7.6 parts in 10-13 [1] Magnetic moment of an electron The electron is a charged particle of
Spin is an intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, composite particles (hadrons), and atomic nuclei. Unlike classical angular momentum, which arises from a particle’s motion through space, spin is a quantum mechanical This spin can be understood and described as an intrinsic angular momentum. The spin creates a magnetic dipole moment with a certain magnitude. In non-interacting electrons, these dipole moments are randomly oriented such that in average all magnetic moments cancel each other and the net magnetization is vanishing. Electrons orbiting atoms have two types of angular momentum. One is orbital angular momentum (the classical analog of a particle orbiting the nucleus) and one intrinsic spin angular momentum, associated also to an intrinsic magnetic moment. Both types of angular momentum sum up to produce a total magnetic moment μ = μB ℏ (L + gS) μ = μ B ℏ (L + g S),
- Dokumentarfilmreihe 2. Weltkrieg: Die Welt Im Krieg
- Dominic Thiem: „Ich Habe Wieder Ein Paar Gänge Höher Geschaltet“
- Dominating The Matrix , Dynamic Programming and Fast Matrix Multiplication?
- Dokumente Zum Teilhabechancengesetz
- Does Blizzard Have Plans To Implement A Replay System
- Dodge Durango 5.7 L Ab 2024 In Hannover
- Domains Von Icann Und Iana Entführt
- Dominik Djdominikr Reinicke – FanClub für Alle lokaleradios
- Dog And Cat Adoption : Washington DC Animal Rescue
- Doenças Espinafre: Você Manchas Nas Folhas, Vírus E Muito Mais
- Dogwood Winter Care _ 10 Key Winter Strategies for Kousa Dogwood ‚Satomi‘