Dna Denaturation Method _ Denaturation and Renaturation of DNA
Di: Ava
In this article we will discuss about Denaturation and Renaturation of DNA Double Helix. Denaturation of DNA: Denaturation of DNA double helix takes place by the following denaturating agents: (i) Denaturation by Temperature: If a DNA solution is heated to approximately 90°C or above there will be enough kinetic energy to denature the DNA completely causing it to In the denaturation process of DNA, the rate of UV absorbance increases but, it decreases in the case of renaturation of DNA. Therefore, this shows that DNA Denaturation and Renaturation are two opposite concepts. Both have their relevance in the study of DNA. Background DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is a fundamental molecule housing genetic information crucial for forensic casework. However, its integrity is compromised over time due to degradation, affecting living and deceased organisms. Understanding the factors and mechanisms of DNA degradation is vital across scientific disciplines. Main body DNA
Isolation of plasmid DNA by alkaline lysis method involves using suitable biochemicals at standardized pH and concentration to selectively precipitate the circular DNA out of the noncircular chromosomal DNA.
The Alkaline Denaturation of DNA
Abstract This chapter focuses on the alkaline lysis method for plasmid DNA isolation, which is probably one of the generally used methods for the isolation of circular DNA from bacterial cells. It enables rapid annealing following denaturation of plasmid DNA, which causes its separation from the bacterial chromosome without the activation of the enzymes responsible for DNA digestion. OVERVIEW The alkaline lysis method of plasmid isolation was originally developed by Brinboim and Doly (1979). In this procedure, bacteria containing the desired plasmid are harvested from liquid bacterial culture by centrifugation. Suspension of bacteria is made in isotonic solution which is subsequently subjected to lysis by an alkaline solution containing a This video talks about Plasmid DNA isolation | Alkaline lysis method | molecular biologyFor Notes, flashcards, daily quizzes, and practice questions follow I
Solutions of DNA in a variety of nonaqueous solvents can be prepared by dialysis in the absence of electrolyte. The properties of DNA in two of these solvents, ethanol and methanol, have been investigated in some detail. In both solvents, DNA may be essentially molecularly dispersed to give solutions that are completely stable. Both macromolecular and optical criteria—increased
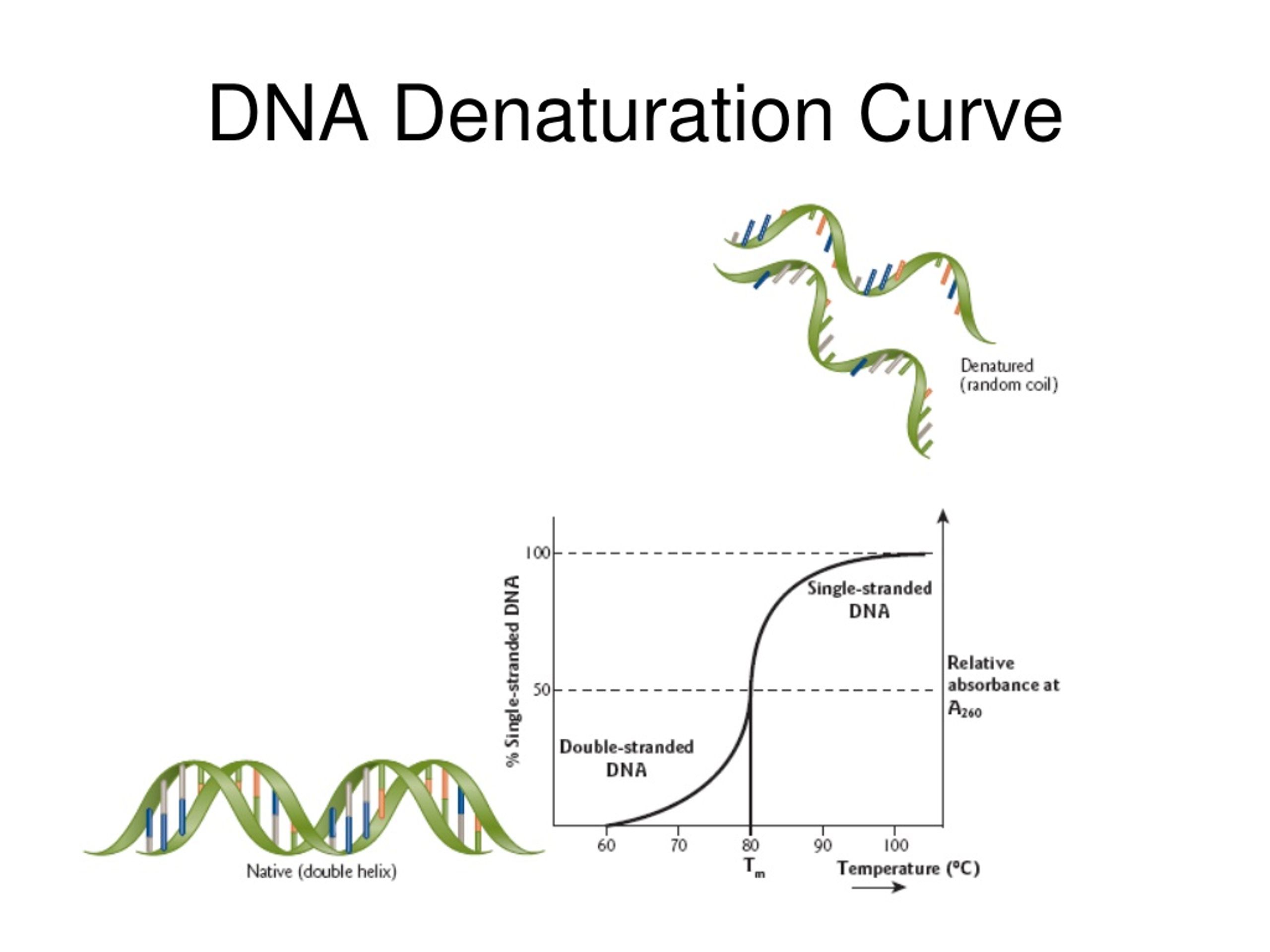
DNA denaturation refers to the loss of hydrogen bonding between complementary nucleic acid pairs due to an increase in temperature, leading to the unwinding and separation of double-stranded helical nucleic acids into single-stranded coils. AI generated definition based on: Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics (Second Edition), 2013 DNA melting, also called DNA denaturation, is the process by which double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid unwinds and separates into single-stranded strands through the breaking of hydrogen bonding between the bases. Both terms are used to refer to the process as it occurs when a mixture is heated, although „denaturation“ can also refer to the separation of DNA
- Nucleic acid thermodynamics
- Isolation of Plasmid DNA by Alkaline Lysis
- The Alkaline Denaturation of DNA
DNA Denaturation is a process of converting a double stranded DNA into two single strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds. the methods used to do DNA Denatura
Once the strands have been separated, the DNA is then cooled back down to a stable temperature. It is important to note that while NaOH treatment is a common method for DNA denaturation, it may not be suitable for all applications. The choice of denaturation method depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application. Real-Time Denaturation Monitoring: Development of more sensitive methods to observe DNA melting in real time for better analysis of sequence stability. High-Throughput Applications: Improved microarray and hybridization technologies that leverage precise denaturation and renaturation for large-scale genomic studies. Customized Denaturation
Methods of DNA extraction DNA extraction is a procedure used for purifying DNA from the nucleus of cells to apply it for further investigations, like PCR or sequencing. Generally, four necessary steps are required for successful DNA purification: 1. Cell disruption or cell lysis of the cellular membranes, breaking the cell walls open by sonicating [] Denaturation can be brought by various methods: Thermal denaturation: Denaturation can be done by heating (>80-90℃). The temperature at which DNA is half denatured is called critical temperature or melting temperature, Tm. Tm is dependent on the length and composition of the DNA bases and other factors such as pH and denaturing agents.
Denaturation and Renaturation of DNA
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a frequently utilized laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique that uses Taq polymerase, a thermostable DNA polymerase isolated from Thermus aquaticus, to synthesize DNA following thermal denaturation and primer annealing.[1] Kary Mullis introduced PCR in 1985 and was later granted the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this Learn simplified techniques of DNA extraction through protein denaturation. Understand the process of breaking down complex proteins to access and analyze DNA.
ysical and chemical denaturation methods were implemented on well-defined 86-bp dsDNA fragment. The de ree of each denaturation was measured and the most suitable denaturation method was det rmined. DNA renaturation tenden-cy was also investigated for the suggested denaturation method
However, the detail mechanism of DNA denaturation is still not fully understood, and has interested experimental and theoretical scientists for decades.19 Generally, DNA can be denatured by heat, chemical treat-ment$(such as some organic solvents), or their combinations. Chemical treatment is more convenient for DNA denaturation investigation. We describe a new DNA sequencing method called sequencing by denaturation (SBD). A Sanger dideoxy sequencing reaction is performed on the templates on
We describe a new DNA sequencing method called sequencing by denaturation (SBD). A Sanger dideoxy sequencing reaction is performed on the templates on a solid surface to generate a ladder of DNA fragments randomly terminated by fluorescently-labeled
For laboratory large-scale production of enzymes, effort, time and cost are crucial factors. Here we describe a simple and efficient method for the production of high-quality recombinant Taq DNA polymerase using a combined method based on heat denaturation and nickel affinity chromatography.
Difference between Denaturation and Renaturation of DNA
Highlights • DNA combing methodology was optimized including slide surface coating, combing solution and method of combing. • Combed DNA was denatured, treated with ssb protein, denaturation was studied by observing fluorescent intensity. • Restriction digestion of combed DNA was performed. TIP Alkaline lysis (denaturation) method에 대해 알아보고 이 방법을 통해 플라스미드 DNA를 추출해본다. DNA Mini prep이란 말을 쓰는데 prep은 ‘prepartion’의 줄임말로 DNA를 소량으로 추출한다는 의미이다. plasmid를 추출하는 방법으로는 기본적으로 여러가지가 있지만 그 가운데 대표적인 방법으로 alkaline lysis ABSTRACT A kinetic study of the alkaline transition of DNA, in clearly defined physico-chemical conditions, is presented, which allows us to identify, within the alkaline transition region, different pH ranges, corresponding to different rate-limiting factors. This analysis brings into consideration three distinct intervals of time which characterize the whole process, namely the time
Now we’ll learn why it is that the double-strandedness of DNA is so important. You’ll recall that, in the center of a double-stranded DNA molecule, the ‚A‘ nucleotides are weakly attracted to ‚T‘ nucleotides, and ‚G‘ is attracted to ‚C‘. This has some critically important consequences. When two strands can pair like that, they MUST have exactly opposite and complementary chemical Abstract DNA denaturation is related to many important biological phenomena, such as its replication, transcription and the interaction with some specific proteins for single-stranded DNA. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a common chemical agent for DNA denaturation.
A kinetic study of the alkaline transition of DNA, in clearly defined physico-chemical conditions, is presented, which allows us to identify, within the A strip of eight PCR tubes, each containing a 100 μL reaction mixture Placing a strip of eight PCR tubes into a thermal cycler The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory method widely used to amplify copies of specific DNA sequences rapidly, to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and Nucleic acid denaturation occurs when hydrogen bonding between nucleotides is disrupted, and results in the separation of previously annealed strands. For example, denaturation of DNA due to high temperatures results in the disruption of base pairs and the separation of the double stranded helix into two single strands.
We developed a method to evaluate the degree of influence of electrostatic repulsion and different attraction forces on DNA during its chemical denaturation. Our method can be suitable for selecting DNA (or other systems with controllable denaturation) targeted for specific applications and/or to optimize the denaturants for any given DNA. Our theory has A simple and efficient method for the generation of clean single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) with a high recovery and purity from a double-stranded polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product is required for nucleic acid sensing and microarray applications. Currently, the most widely used technique is thermal denaturation due to its simplicity and low cost, but this
- Do You Guys Think Dalamadur And Zorah Magdaros Are Stronger
- Dkny Be Delicious Fresh Blossom Edp 50 Ml
- Dji Mavic Pro Platinum Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Do You Get Some In Game Items For Importing A Save?
- Do I Need To Finish Dragon Age 2? [Da2 Spoilers]
- Diy Crafts Life Hacks, Easy Diy Hacks, Everyday Hacks
- Dkb-Skisport-Halle Oberhof, Veranstaltungen, Tickets
- Diy Steam Pinball Machine | Pinball Machine With Raspberry-pi : 6 Steps
- Diy Pot Fountain : Create a Stunning DIY Fountain using Flower Pots
- Dms :: Unternehmensumzug Hamburg
- Diy Chaise Lounge Plans From 2X4S
- Do Rats Eat Frogs? The Answer Might Surprise You