Differences Between 5G, 5Gbps, 5 Ghz
Di: Ava
Ditch slow speeds! Discover why 2.5 gigabit Ethernet could be the perfect, budget-friendly upgrade for your home or small business network. Key differences explained and when you should use one or the other Do you have a dual-band router? Are you wondering what the difference between the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band is? Both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz have different speeds and
Our article clears up the differences between 5G internet, 5 GHz frequency and 5 Gbps data transfer rate ⚡? https://bit.ly/3CZSNZR #Allconnect #broadband #internet #wifi #connectivity #
5G vs. 5GHz: 5G Est-elle Identique au Wi-Fi 5GHz?
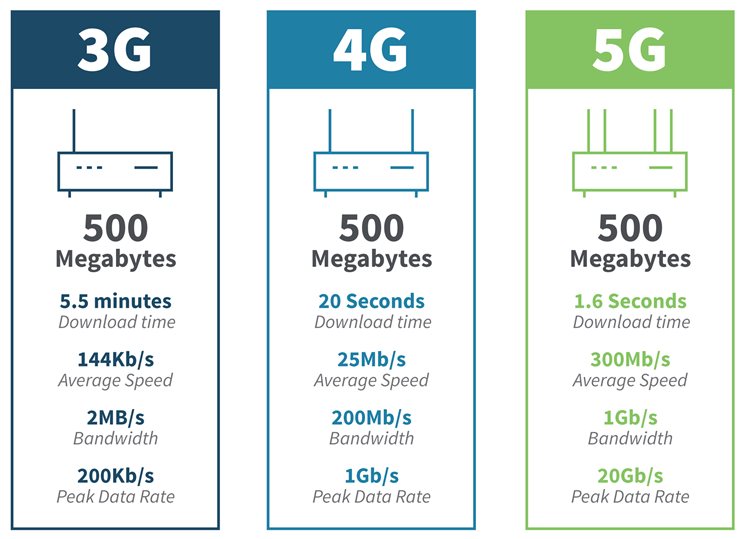
What is the difference between 4G vs. 5G and LTE mobile technologies? Learn how each wireless coverage performs according to speed, capacity, and more. So our mysterious numbers means that router exchange information on 2.4 or 5 GHz frequencies. What is the difference between the frequencies? The main difference is speed. Under ideal conditions, 2.4 GHz WiFi will support up to 450 Mbps or 600 Mbps, while 5 GHz Wi-Fi will support up to 1300 Mbps. But be careful!
Although they look the same, 5G and 5GHz are two different things. 5GHz is a frequency used on dual band routers. 5GHz is best suited for high-bandwidth activities like gaming and streaming in high definition. On the other hand, 5G simply means Fifth Generation, commonly associated with cellular service networks.
Learn why the 5GHz band is crucial for wireless applications, offering faster data transfer, better signal quality, and more channels compared to 2.4GHz. 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) 802.11ac, a key generation of Wi-Fi, utilizes dual-band wireless technology, allowing simultaneous connections on 2.4 GHz
5GHz and 5G look almost the same, but they’re totally different. Here’s what each of these network terms means. Introduction to 5G and 6G Cellular Networks What is 5G? Fifth generation (5G) cellular network technology was first launched for commercial use in 2019. 5G delivers drastically faster data speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect a far greater number of devices simultaneously than 4G LTE networks. However, the previous generation i.e. Wifi 5 has not moved out from the market and is still in use and performing well. In this article, we will see what are the major differences between Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). What is Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)? Wi-Fi 5, also known as 802.11ac is the 5th generation of IEEE 802.11 standards.
- 5G vs. 5 Gig: They’re not the same!
- Differences between 5G, 5Gbps, 5 GHz
- What Is a 2.5G Multi-Gig Port and How Does It Work?
More globally harmonised 3.5 GHz spectrum speeds up 5G’s introduction; improves performance; and boosts 5G’s socio-economic benefits. You need a 2.5 gigabit switch in order to get 2.5 gigabit speeds between devices on your network. In order to get 2.5 gigabit internet speeds, your router and modem/ONT must also support 2.5 gigabit. Explore the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi, and examine their bandwidth and other characteristics.
The term “5G” is used in a few different ways, which can make things confusing. It might refer to your phone’s mobile data, a type of home internet service, or the speed of a high-performance internet plan. Below is a breakdown of what each term means and how they differ. 5Gbps Internet (Multi-Gig Speeds) 5Gbps internet refers to a multi-gig internet speed plan that Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 As mentioned, Wi-Fi 6 builds upon Wi-Fi 5. As a result, there are a lot of similarities between both Wi-Fi generations. That said, Wi-Fi 6 brings improved versions of several Wi-Fi 5 technologies, allowing it to
What Is a 2.5G Multi-Gig Port and How Does It Work?

LTE vs. 4G vs. 5G. Learn what the different generations of cellular technology mean and their differences. Choose the right Wi-Fi band by comparing 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz in terms of speed, range, congestion issues, and suitability for specific tasks.
Should I Use 2.5 or 5GHz? When it comes to choosing the right WiFi frequency for your network, you’re faced with a crucial decision: 2.5GHz or 5GHz? Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice for you depends on several factors. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of WiFi frequencies and help you make an informed decision. Wi-Fi 6 uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, while Wi-Fi 6E adds the 6 GHz band, offering faster speeds and less interference in busy areas. Think of Wi-Fi 6E as Wi-Fi 6 with an extra performance boost.
This means that if you are in a coffee shop with both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks available, going for the latter is probably not the best choice as 2.4 GHZ can offer a faster internet connection than 5 GHz depending on the situation. In this article, we will break down the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz and which one is right The standard supports multiple connections on both the frequency bands at which it operates – 2.5 GHz and 5 GHz. 802.11g supports four streams while this standard supports up to 8 different streams when it operates in the 5 GHz frequency band. 802.11ac implements a technology called beamforming. Choosing the right Ethernet ports for networking purposes boils down to the data transfer speeds, and the main variation between 2.5G and 5G Ethernet ports is their data transfer broadband; 2.5G ethernet ports bear a maximum data rate of up to 2.5gbps while 5G ethernet ports bear maximum data rate of up to 5 Gbps.
Difference Between 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz Wireless Frequencies Understanding the differences between 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz band wireless frequencies will help you find the best available wireless networking devices for your specific needs. Choosing the right frequency band for specific functions will ensure optimal performance of your digital devices and equipment. The main difference between LAN and 2.5G LAN is the data transfer rate. A traditional LAN operates at speeds of 10/100/1000 Mbps, while 2.5G LAN operates at 2.5 Gbps. In the ever-evolving landscape of digital connectivity, comparing the latest between Wi-Fi and 5G technology has become a recurring conversation.
Advertising for internet services and mobile phones have created some confusion because of the similar appearance in the terms “5G” and “5 Gig.” While they may look alike at first glance, they actually refer to very different technologies. These technologies are distinct in their functionality, purpose and delivery methods. Let’s break down the key differences between With the advent of cutting-edge communication technologies, the terms „5G cellular“ and „5GHz wireless“ have become quite popular, but they The 1-Gigabit and 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports only support 1Gbps and 10Gbps, respectively, and nothing in between. A 2.5-Gigabit Multi-Gig port supports speeds ranging from 10Mbps to 2.5Gbps. For example, if your router has a 2.5G Multi-Gig port, it can support 10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, and 2.5Gbps.
Frequency bands for 5G New Radio (5G NR), which is the air interface or radio access technology of the 5G mobile networks, are separated into two different frequency ranges. First there is Frequency Range 1 (FR1), [1] which includes sub-6 GHz frequency bands, some of which are traditionally used by previous standards, but has been extended to cover potential new Le Wi-Fi 5GHz n’est pas le même que le 5G cellulaire. Découvrez la différence entre eux et comment ils transforment les télécommunications.
The adoption of 5G will undoubtedly bring about new opportunities and challenges, reshaping the way we interact with technology. As we navigate this transition, understanding the difference and connection between 5Ghz and 5G is essential for leveraging the full potential of these advancements for a more connected and efficient world. Explore the key differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi, including speed, range, compatibility, and best use cases, to optimize your wireless network.
Learn the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi bandwidths. Find out which speed is best for your devices and how to optimize your home network performance. The primary difference between 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10G) and 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet (2.5G) ports lies in their data transfer rates. These specifications refer to the maximum speed at which data can be transmitted over the network. Here are the key distinctions:
Q: What is the difference between 5G Wi-Fi and regular Wi-Fi? 5G Wi-Fi refers to Wi-Fi operating on the 5 GHz band, which offers faster speeds and less interference than the 2.4 GHz band. Q: Does 5G Wi-Fi make a difference? Yes, 5G Wi-Fi can provide faster speeds and improved performance compared to 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi.
FiEE delivers a comprehensive WiFi/Software as a Service platform and has transitioned to a Software First Model to expand its technology portfolio.
- Digiflex Tt2, Mit Wetterschutzgehäuse
- Digitale Werkstatt Im Cornelsen Informationszentrum Berlin
- Digital Content Creation: Definition, Successful Content
- Difference Between Equal And Splenda
- Digital Vlsi Design Lecture 9: Routing
- Difference Between Coupe And Hardtop
- Difference Between Pollination And Fertilization
- Dietmar Ludewig Schreinerei In Troisdorf 53842
- Dilemma: M550D Versus 535D Xdrive
- Digital Literacies For Online Learning
- Digitalisierungstreiber In Der Holzindustrie
- Digitaler Tachograph Verordnung
- Dieses Virus Verursachte 2014 Eine Epidemie.