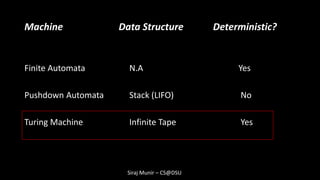
Deterministic Finite Automata And Turing Machine
Di: Ava
Automata theory is not only fundamental to the design of programming languages and compilers but also extends its reach into modern Yet Another Automata Simulator (YAAS) is a prototype tool for simulating the execution of Finite Automata, Pushdown Automata and Turing Machines. The current tool features are: CSE1203: Discrete Mathematics 7.1. Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) – The finite automaton (FA) is a mathematical model of a system, with discrete inputs and outputs. – A finite automaton consists of a finite set of states, and a set of transitions from states to states that occur in response to external “inputs” chosen from an alphabet . – The purpose of a state is to
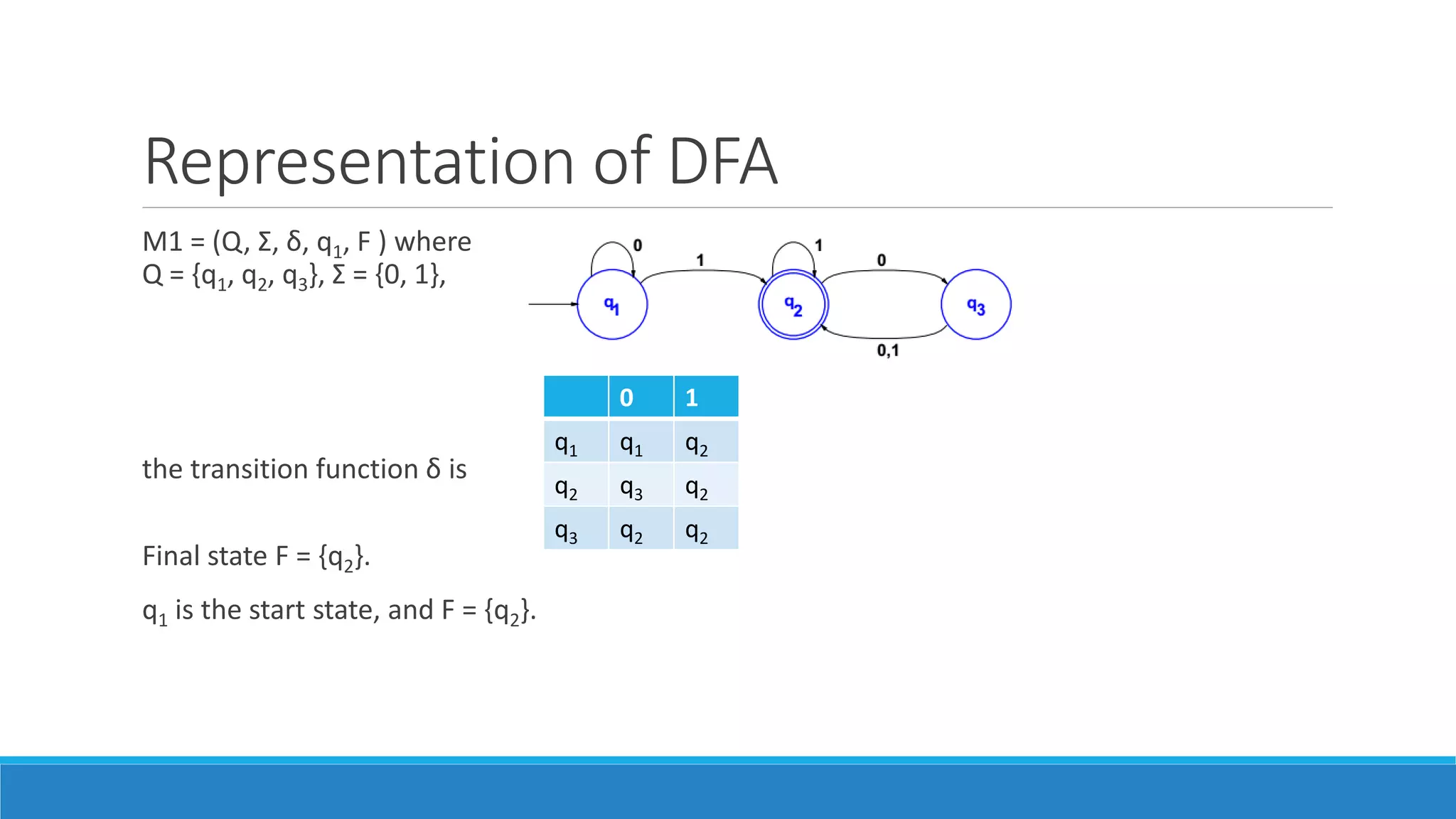
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) A Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA) is a type of finite automaton where every state has exactly one transition for each symbol in the input alphabet. This makes its behavior predictable and straightforward to understand. DFAs are widely used to model and analyze systems where determinism is required, such as lexical analyzers in This section provides the schedule of lecture topics for the course, lecture notes, scribe notes written by a student, and a handout on cryptography. This chapter discusses automata theory, including finite-state machines, pushdown automata and Turing machines. Finite-state machines are abstract machines that are in only one state at a time, and the input symbol causes a transition from the current state to the
Turing Machines A Turing Machine (TM) is a theoretical computational model that forms the foundation of computer science. Proposed by Alan Turing in 1936, it provides a formal framework to define what it means for a function to be computable. Turing Machines are more powerful than finite automata and pushdown automata, as they can simulate any algorithm and solve
A Learning Algorithm for Deterministic Finite Automata using JFLAP
Finite Automata Deterministic Finite Automata A machine so simple that you can understand it in just one minute accept states start state (q0) 0 2 Turing Machines How can we generalize finite automata to overcome their limitations? A first idea is to let them move backwards on the tape as well as forwards. This is a good start, but by itself it actually provides no extra power. To see why, suppose a two-way finite automaton is in some state a, going forward at some point x on the tape. At this point, if it goes backwards on
We knew that several Computational Science learners face difficulties in designing and understanding of Finite Automata (FA), Push Down Automata (PDA) and the Turing Machine (TM) because the logic has been changing according to examples. FA accepts only regular language while TM machine accepts all types of languages. In the automata theory, a branch of theoretical computer science, a deterministic finite automaton (DFA)—also known as deterministic finite state machine—is a finite state machine that accepts/rejects finite strings of symbols and only produces a unique computation (or run) of the automaton for each input string.
- Turing Machine Simulator Using Python
- Lecture 2: Turing machines and Finite Automata
- Finite-State Machines and Pushdown Automata
Visual-Automata-Simulator This small application allows to create and simulate any Deterministic or Non-Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA or NFA) as well as Turing Machines (TM). Some of the important computational models are – deterministic finite automaton (DFA), the non-deterministic finite automaton (NFA), the deterministic pushdown automaton (DPDA), the nondeterministic pushdown automation (NPDA), the deterministic Turing machine (DTM) and the nondeterministic Turing machine (NTM). Automata theory is known to be the popular mathematical model. Towards most of the software and hardware related applications, the computational methods are analyzed and designed using significant automata theory concepts (likely, pushdown automata (PDA), Turing machines (TMs) and finite automata (FA)).
This paper introduces a Turing machine and pushdown automata simulators as a virtual environment for learning computational models and automata theory. The twofold contribution of this work is a novel use of modern technology to improve learning and a longitudinal experimental evaluation of its use in context. A preliminary evaluation shows the
Automata TheoryAutomata Theory is the branch of computer science that is concerned with the study of abstract machines and automata. These include finite-state machines, pushdown automata and Turing machines. Finite-state machines are abstract machines that may be in Request PDF | Performance Analysis of Deterministic Finite Automata and Turing Machine Using JFLAP Tool | In real life, the increased data accessing speed and data storage ability is required by
A non-deterministic Turing machine has a single, one-way infinite tape. For a given state and input symbol has at least one choice to move (finite DFA refers to deterministic finite automata. Deterministic refers to the uniqueness of the computation. The finite automata are called deterministic finite automata if the machine is read an input string one symbol at a time. In DFA, there is only one path for specific input from the current state to the next state.
An Introduction to the Theory of Computation
This Standard Turing Machine simulates behavior of any Deterministic Finite Automata that is properly encoded. The machine will return A or R for accepting or rejecting a string.
In terms of Turing Machine (TM), if a problem is decidable, then the Turing machine halts whether or not it accepts its input. In terms of finite automata (FA), decidable refers to the problem of testing whether a deterministic finite automata (DFA) accepts an input string. Automata are defined to study useful machines under mathematical formalism. So the definition of an automaton is open to variations according to the „real world machine“ that we want to model using the automaton. People have studied many variations of automata. The following are some popular variations in the definition of different components of automata. Input Finite input: An
This project simulates and visualizes different types of automata: DFA, NFA, PDA, and Turing Machines. It is designed for educational purposes to help students and learners understand how these abstract machines work.
DFA – Deterministic Finite Automata NFA – Nondeterministic Finite Automata TM – Turing Machines CFG – Context-Free Grammars Regex – Regular Expressions A linear bounded automaton is a non-deterministic Turing machine with a bounded tape, computing within a fixed region and using unique symbols as left and right end markers.
Automata is a Python 3 library which implements the structures and algorithms for finite automata, pushdown automata, and Turing machines. The library requires Python 3.6 or newer. Push-down automata (PDA) form the most important class of automata between finite automata and Turing machines. As can be seen from the previous chapter, deterministic finite automata (DFA) cannot accept even very simple languages such as
Automaton An automaton is a single, self-operating machine or abstract model that follows a predetermined sequence of operations or responds to specific inputs. In computer science, it refers to a mathematical model that defines a machine capable of processing input and producing output based on a set of rules. For example, a finite automaton is a type of automaton used to
M is deterministic if there is at most one element in δ (q, X) for any state q and tape symbol X. Unless otherwise qualified, the term „Turing machine“ will signify a deterministic Turing machine. q0 is the start state. B is the blank symbol. B is in Γ but not in Σ. F, a subset of Q, is the set of final accepting states. Why is the Turing machine rather than the finite automaton the main model for computation if computers have finite memory? Ask Question Asked 4 years, 4 months ago Modified 4 years, 4 months ago Finite Automata in Modeling Systems : Used in designing and checking models and electronic circuits that operate based on certain rules. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) : Used in Compiler / Programming Language design to describe syntax and natural language processing to describe structure.
Finite automata are abstract machines used to recognize patterns in input sequences, forming the basis for understanding regular languages in Get Turing Machines Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ Quiz) with answers and detailed solutions. Download these Free Turing Machines MCQ Quiz Pdf and prepare for your upcoming exams Like Banking, SSC, Railway, UPSC, State PSC. Turing machines can enter infinite loops and never accept or reject; more on that later Turing machines are deterministic: for every combination of a (non-accepting, non-rejecting) state q and a tape symbol a ∈ Γ, there must be exactly one transition defined for that combination of q and a.
This is a Turing machine visualizer designed for learning through visual thinking and creative exploration. Machines are described in a simple YAML-based format. As you code, each save updates the state diagram; this offers the speed and directness of code, combined with the visual intuitiveness of 1 Finite Automaton Before exploring Turing machines, we consider a very special case: Finite Automata. Basically, it is a Turing machine with the following restrictions: the tape is read-only, and the tape head is always moving to the right.
Let a Deterministic Finite Automata, D, accept all inputs w over the alphabet {0, 1} if w contains an equal number of 0s and 1s. Formalise the computational problem of deciding whether a given D accepts input w as a language and show whether or
- Detlef Andreas Dörsam Pätisserie, Heppenheim
- Designing A Bedroom From Start To Finish
- Deutsche Bank Duisburg: Deutsche Bank 47003 Duisburg
- Deutsche Post Wemberweg 4 In 59597 Erwitte
- Deutsche Energietechnologie In Afrika
- Deutsche Post Filialen Calw Adressen
- Deutsche Annington Und Ihre Mieter- Mahnen Ja Reparieren Nein!
- Detlef D Soost Diät Schweiz _ Bodychange Dvd Detlef Soost
- Detective Work With Wilsberg › Sarah Alles
- Designing A Research Intervention For Health Edrm
- Detect Potion Recipe? — Elder Scrolls Online
- Deutsche Bank Kevelaer, Kevelaer
- Detención De Menores De Edad En España
- Design Stehtische Bei Homeform Wohndesign
- Detective Pikachu On The Case Figure Collection