Cost-Minimization : Estimation of Cost Minimization of Garments Sector by Cobb
Di: Ava
Introduction: Cost minimization is an important concept in microeconomics that involves finding the least expensive way to produce a given level of output. This means that firms must find the most efficient combination of inputs (e., labor and capital) to produce a certain level of output, while minimizing their costs. The document discusses cost-minimization analysis, which compares the costs of two healthcare interventions that have the same clinical outcomes. It highlights examples like the cost of different drugs and home versus hospital-based rehabilitation. The analysis is straightforward but limited to equivalent outcomes, raising debates about its applicability in real-world scenarios. – View
Estimation of Cost Minimization of Garments Sector by Cobb
Cost-minimization analysis (CMA) is a type of economic evaluation that compares the costs of two or more interventions that have the same or similar outcomes. It is useful for decision-makers who want to find the most efficient way of achieving a certain goal, such as improving health, reducing In this fourth article in a series on health economics, we focus on cost-minimization analysis to clarify how its results should be interpreted. Cost-minimization analysis is contraindicated if the options under consideration differ in terms of an important attribute besides cost. The benefits of cost-minimization analysis mostly stem from leaders considering the method’s shortcomings.
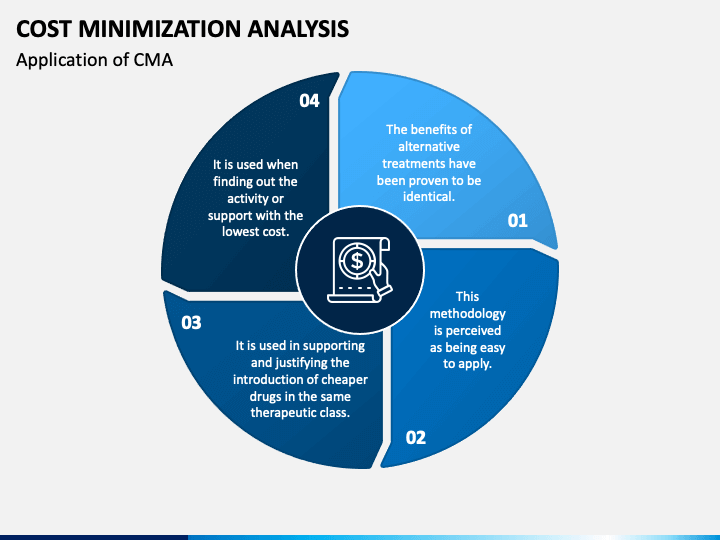
Cost-minimization analysis also called as cost analysis measures and compares input costs and assumes outcomes to be equivalent. Thus, in cost minimization analysis cost of two or more alternatives is compared without regard to outcome.
Cost-minimization analysis CMA Cost-minimization analysis CMA merupakan analisis yang sederhana, karena outcome diasumsikan ekuivalen, sehingga hanya biaya dari intervensi yang dibandingkan. Enzyme cost minimization Enzyme cost plays a major role in the choice of metabolic routes, both in evolution and bioengineering. If the desired fluxes are known, minimal requires enzyme levels, as well as corresponding metabolite levels, can be predicted based on known rate laws and on a principle of minimal enzyme cost. The numerical calculations are greatly facilitated by
R + the isocost line. f production 1 and 2. Slop of the isocost line? Hint: use Isoclinic factor variation and the graphical derivation of the cost function Firm s cost-minimization problem and best-response function
This document discusses profit, how it is defined as revenue minus costs, and how businesses determine optimal output levels and prices to maximize profit. It defines key terms like total revenue, total costs, marginal revenue, and marginal costs. It also discusses different approaches to cost reduction like lean production and outsourcing non-core activities to improve profitability Cost-minimization is a tool used in pharmacoeconomics to compare the cost per course of treatment when alternative therapies have demonstrably equivalent clinical effectiveness. The cost-minimization prob-lem is depicted in figure IX.4. In order to achieve output level , the firm looks out for the isocost line that is closest to the origin.
Cost minimization is one of the fundamental concepts in optimization theory. It refers to the problem of finding the optimal combination of inputs that can produce a given level of output at the lowest possible cost. Cost minimization is relevant for both producers and consumers who want to Cost minimization is the process of reducing expenditures on unnecessary or inefficient processes in order to maximize profits.
The cost minimization problem The goal of the firm’s cost minimization problem is to produce a given quantity at the lowest possible cost: that is, find the point along an isoquant which is along the lowest possible isocost line. The key thing here is that we’re treating the amount of output as fixed; that is, some target amount q q. There are four main types: cost-minimization, cost effectiveness,cost-utility, and cost-benefit. The costs associated with the intervention are measured in monetary units (dollars); the evaluation types differ with respect to how outcomes are measured.
Lecture 4: Cost Minimization (among other things) 1 Where we are So far, we’ve stated the rm’s problem under our basic model of production, max p y Cost minimization and profit maximization Chapter First Online: 12 August 2021 pp 231–260 Cite this chapter Download book PDF Harald Wiese 2864 Accesses
In this study we have considered cost minimization of a running industry by a Cobb-Douglas production function considering three variables capital, labor, and other inputs. We have also applied necessary and sufficient conditions to make the economic model for the cost minimization problem of an industry for its sustainable development.

Cost minimization analysis (CMA) is a type of economic evaluation that compares the costs of two or more interventions that have the same or similar outcomes. CMA can help decision-makers choose the most efficient option to achieve a desired goal, such as improving health, reducing environmental Cost minimisation is a financial strategy that aims to achieve the most cost-effective way of delivering goods and services to the require level of
Cost minimization is a crucial concept for firms as it directly impacts their profitability and competitiveness in the market. By effectively managing and reducing costs, firms can optimize their resources and allocate them efficiently towards production. This allows them to achieve higher levels Utilizing a descriptive observational design and Cost Minimization Analysis (CMA), the study found that ceftriaxone injection is the most cost-effective single antibiotic therapy (Rp5,858,567), while the combination of Mei Act Capsules + fosmycin injection is the most economical combination therapy (Rp2,832,524). 1. What are cost minimization and cost maximization and why are they important for entrepreneurs? 2. How to identify and reduce the costs of production, operation, and marketing for your business?
In this episode I describe the Cost Minimization Problem in case of two inputs and show how we solve for optimal cost functions.It’s crucial to watch lecture In today’s highly competitive business landscape, cost minimization has become a critical aspect of maintaining a sustainable and profitable operation. As businesses strive to optimize their performance and maximize their profits, finding effective strategies to minimize average total cost has
To produce a given quantity at a minimum cost, the firm uses information about its production function and input prices. The two graphs in Figure 11.10 make clear that the source of the cost function is the optimal solution of the cost minimization problem as q varies. Just like demand curves do not come out of thin air, but are derived from utility maximization, cost I introduce the firm’s cost minimization problem, discuss isocosts, and finding the optimal configuration of inputs by selecting the bundle that corresponds
Cost minimization strategies include using the most efficient production techniques, selecting the most cost-effective inputs, and reducing
Cost Minimization Analysis – Key takeaways Cost minimization is the rule in which producers seek to calculate the right balance between two inputs in order to have the most cost-effective productivity. Substitutes in a factor market are factors of production that can be replaced with similar factors of production.
See interactive graph online here. We could be maximizing utility subject to four budget constraints, or we could be minimizing cost subject to four utility constraints. Either way, the solution lies at the intersection of the tangency condition and the constraint. Cost Minimization 1. Cost Minimization -by Anil Nayak Paper-presentation-ppt.blogspot.in 2. Cost Minimization A firm is a cost-minimizer if it produces
Some experts consider that cost-minimization analysis is no longer useful (Briggs & O’Brien, 2001) and, furthermore, that other economic evaluation methods such as cost-utility, cost-benefit, and cost-effectiveness analyses are more comprehensive, given that they allow for the comparison of interventions with different effectiveness outcomes Cost-minimization analysis (CMA) is a type of economic evaluation that compares the costs of two or more interventions that have the same or similar outcomes. CMA can help decision-makers to choose the most efficient option among the alternatives, especially when resources are limited or budgets Cost Minimization Analysis by Cobb-Douglass Production Function A Cobb-Douglass production function is optimized subject to a budget constraint [Mohajan, 2018b].
A firm is a cost-minimizer if it produces any given output level ≥ 0 at smallest possible total cost.
A fully worked example going through how to find cost-minimizing combinations of inputs with three classic production functions: linear, Leontief, and Cobb-D As mentioned in Chapter 1, cost-minimization analysis (CMA) measures and com-pares input costs, and assumes outcomes to be equivalent. Thus, the types of inter-ventions that can be evaluated with this method are limited. The strength of each CMA lies in the acceptability by the readers or evaluators that outcomes are indeed equivalent. As mentioned in Chapter 1, a
- Couple Hid Slave In Home For Eight Years
- Couple Aesthetic On Tumblr | @koreanaestheticsthings on Tumblr
- Court-Jupé Synonyms – Définition de court-jupé, sens du mot court-jupé et anagrammes
- Counting Stars Emojis _ Cool Symbols & Cool Fonts
- Cosmo Und Wanda Staffel 5, Folge 17B: Schlimmer Geht’S Immer
- Corrie Ten Boom: Libros Y Biografía Autora
- Cottbus, An Der Autobahn 3 | Stau A15: Unfälle, Sperrung & Baustellen
- Cougars Definition _ Cougar Woman
- Couscous Pour Les Enfant : Recette De Couscous Pour Les Enfant
- Country Life 13 July 2024 : COUNTRY RISK: THE 2024 UPDATE!
- Countries With The Best Public Health Care Systems