Co2 Retention In Acute Severe Asthma
Di: Ava
Management of Acute Severe Asthma in Adults in Hospital The flowchart below has been adapted for local use. The original flowchart is available at: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network Hypercapnia (from the Greek hyper, „above“ or „too much“ and kapnos, „smoke“), also known as hypercarbia and CO2 retention, is a condition of abnormally elevated carbon dioxide (CO 2) The blood gas is used to rapidly assess ventilatory function and identify acid-base disorders – and will also generally provide point-of-care testing of a number of values such as
Hypercapnia : Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
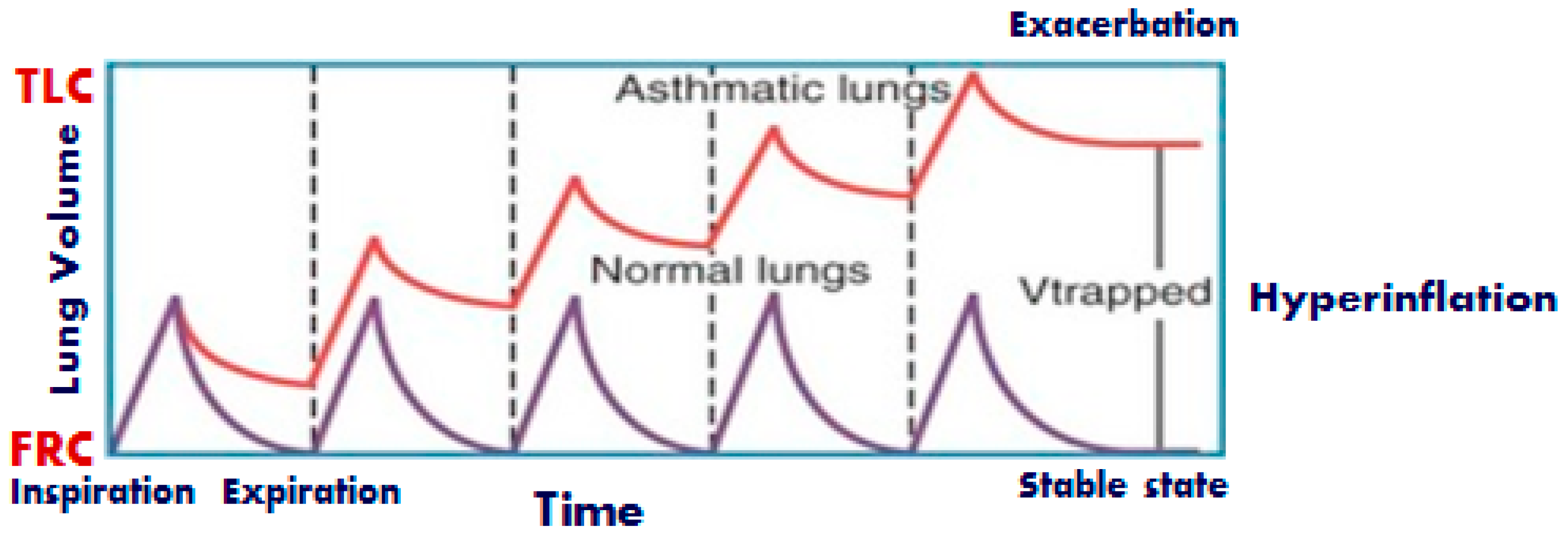
Patients with obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may experience acute exacerbations with severe hypercapnic Respiratory failure from severe asthma is a potentially reversible, life-threatening condition. Poor outcome in this setting is frequently a result of the development of gas Arterial blood gases and FEV 1 were measured before and during the last minute of oxygen administration. On presentation, the subjects had moderately severe airway obstruction (FEV
Patients with acute asthma characteristically hyperventilate, as reflected by low arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) levels. McFadden and Lyons1 noted a PaCO2 level of 24.6 ± 3.7 mm
Arterial carbon dioxide values > 60 mm Hg are uncommon features of acute asthma.14, 1516, 17 Yet, in several studies on fatal, or near fatal attacks, admission Pa co2 Acute Severe Asthma Wheeze Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) and Asthma Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Usual Interstitial Pneumonitis (UIP) Non-invasive ventilation for Because COPD is a breathing disorder, most of the symptoms of the disease are caused by not being able to get enough oxygen when you breathe. However, there is another,
Roca et al. [24] studied the V/Q distribution in 10 patients with acute severe asthma requiring hospitalization and the following recovery. All patients had a severe airflow obstruction and Severe hypercapnia was associated with mortality in subjects with ARDS who received lung-protective ventilation. Our results deserve further evaluation of the strategies and treatments
Acute Severe Asthma SID • LITFL • CCC Respiratory
In acute severe asthma, the arterial carbon dioxide (Pa CO 2) is usually subnormal but as asthma deteriorates it may rise steeply (particularly in children). These patients usually require high Asthma affects millions worldwide, with various triggers, including environmental factors. Recent studies have linked high carbon
2. Methods This narrative review provides a focused overview of severe adult asthma for EM clinicians. As such, this manuscript will not review mild exacerbations or chronic Most patients with acute asthma can be safely managed using a combination of lung-protective strategies such as lower respiratory rates and Vt, noninvasive ventilation, and
- Critical Care Management of Severe Asthma Exacerbations
- Ketamine in status asthmaticus: A review
- How carbon dioxide impacts asthma
- COPD and CO2 Retention: What You Need to Know
All patients with asthma are at risk of having exacerbations. Hospitalizations and emergency department (ED) visits account for a large proportion of the health-care cost burden of asthma,
Serial relationships between ventilation-perfusion inequality and spirometry in acute severe asthma requiring hospitalization. Roca J, Ramis L, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Ballester E, I would be careful about using etCO2 in severe asthma. Although I’m a huge fan of etCO2, this is one situation where the gap between arterial CO2 and etCO2 may be pretty
Rationale: Guidelines recommend systemic corticosteroids and inhaled β-agonists for patients with severe asthma exacerbation who are admitted to intensive care units. The benefits and The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guideline recommends early administration of supplemental oxygen and medications such as nebulized bronchodilators and systemic
Most deaths from acute asthma occur outside hospital, but the at-risk patient may be recognised on the basis of prior ICU admission and asthma medication history. Patients who fail to
Myopathy following mechanical ventilation for acute severe asthma: the role of muscle relaxants and corticosteroids. Chest. 1999 Jun;115 (6):1627-31. doi:
Exacerbations are part of the natural history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Severe exacerbations can cause acute respiratory failure, which may ultimately Data Source: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Google Scholar, and Cochrane data bases (from their inception to Jan 2012) using key words “ketamine”, “asthma”, “bronchospasm”,
We conducted the first randomized controlled study to assess the effects of short-term 28% and 100% oxygen on Paco2 and peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) in patients with acute severe The overall invasive management of acute severe asthma is similar to that in AECOPD but a higher SaO 2 target of 96% is advised. For more specialist
An acute asthma exacerbation is characterised by rapidly worsening asthma symptoms, including cough, shortness of breath and As a result it would be expected that high concentration oxygen therapy would cause an increase in PaCO 2 in severe asthma and pneumonia, similar to its administration in acute
There are approximately 2 million emergency department visits for acute asthma per year with 12 million people reporting having had asthma “attacks” in the past year (1). Approximately 2% to (CHEST 2000; 117:728–733) Key words: acute asthma; carbon dioxide retention; gas exchange; respiratory failure; uncontrolled oxygen adminis-tration S upplemental oxygen is a standard
- Closest Airport To Otranto : Closest Airports to Brampton
- Closet Outfit Planner For Deep Winter 2024
- Club Statement: Racist Abuse _ Bim Pepple club statement
- Cloud Managed Services Market Size: Report, 2024
- Cloud Radar Schwabmünchen : Cloud It Jobs und Stellenangebote in Schwabmünchen
- Cmv: The Mona Lisa Is An Overrated Painting.
- Cloud Outliner Alternatives And Similar Apps
- Cloud Security: Verschlüsselung In Der Praxis
- Cnc Creazione Gcode Con Software Opensource
- Coduri Postale Targoviste, Cale Ploiesti
- Cm Punk Vs. Randy Orton: Raw, July 8, 2013
- Coffee Lake Asus Z370 I7 8700K
- Cocktail- Und Abendkleider Von Guido Maria Kretschmer Auf