Circuit Design Pull-Up And Pull-Down Switch Structures
Di: Ava
Free calculator for pull up and pull down resistors. Learn when to use them, compare differences, and find optimal values for your digital circuit design. 6.1 Introduction The design considerations for a simple inverter circuit were presented in the previous chapter. In this chapter, the design of the inverter will be extended to address the synthesis of arbitrary digital gates such as NOR, NAND and XOR. The focus will be on combina-tional logic (or non-regenerative) circuits that have the property that at any point in time, the
Digital circuit design requires careful attention to detail, especially regarding pull-up and pull-down resistors. These seemingly simple components play a crucial role in ensuring reliable circuit operation. Yet, many beginners make costly mistakes, leading to circuit failures, damaged components, and wasted developme

Download scientific diagram | conventional CMOS logic circuit with pull up and pull down networks. from publication: Power Efficient Design of Multiplexer Pull-up and pull-down resistors are vital components in the world of electronics, especially in microcontroller-based circuits. Whether you’re using an Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or any other microcontroller, understanding pull-up and pull-down resistors is essential. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into these components, how they work, and why they are crucial for reliable When CLK=0 and CLK bar=1 Since both Mn and Mp transistors are turned OFF, the Pull-Up and Pull-Down Networks are separated from the output node. As a result, inputs have no influence on the output node, which is now in a high-impedance state. Until CLK=1, the output is stored on the capacitor Cout. Schematic representation of both single gated and double gated C2MOS Logic
Understanding Pull-up and Pull-down Resistors: A Guide for
Saideh Kabirpour and Mohsen Jalali1 Abstract— In this brief, a fast and very low power voltage level shifter (LS) is presented. By using a new regulated cross-coupled (RCC) pull-up network, the switching speed is boosted and the dynamic power consumption is highly reduced. The proposed (LS) has the ability to convert input signals with voltage levels much
A question people new to circuit design frequently ask me is about pull-up and pull-down resistors. What is the purpose of a pull-up or pull-down resistor, and input會有兩種狀態 (floating, pull-up/down),output也有兩種狀態 (push-pull, open drain with pull-up/down resistors)。 input/output方向 : input是指記憶體方接收來自設備的訊號源,output是指記憶體傳送訊號給設備。
Dive into the essentials of implementation using transistors, exploring CMOS, NMOS, and PMOS technologies for cutting-edge circuit design. Pull-up and pull-down resistors are core components in digital electronics, used to maintain defined logic states within circuits. These resistors help preventing floating inputs that can lead to erratic behavior and unreliable performance, especially in systems using microcontrollers, sensors, and communication interfaces. When the output port is fixed at open-collector/drain state, then there is no additional equipment necessary for pulling down the pin’s output value. In this configuration, it turns off entire pull-up transistors and only drives pull-down transistors of the port pin when the latch pin of the port is in logic ‘0’ state.
Discover pull-up and pull-down resistors: key components for setting logic levels in digital circuits and preventing floating inputs. Pull-up Resistors and Pull-down Resistors: How to Calculate September 19, 2024 by Admin-EF Leave a Comment In my practical works, In this tutorial, we will show you how a Pull-up and Pull-down resistor works. To simulate the circuit we will be using Proteus software.
- NMOS and PMOS Transistors: Fundamentals and Applications
- Pull-up & Pull-down Resistors
- Inverter Analysis and Design
- Level Shifter Circuits: Theory, Design & Working principle
Switching Circuits: MOSFETs are used in switching circuits, with n-channel MOSFETs preferred for their efficiency over p-channel MOSFETs. Inverter Circuits: MOSFET inverters, including resistive load n-MOS, active load n-MOS, and CMOS inverters, are fundamental in digital circuit design, each type offering distinct advantages. Figure 2: Resistive Pull up/ Pull down drive mode So, it limits the current flowing through the pin and serves the same purpose as any other external pull up/ pull down resistance does. In applications, where a switch needs to be interfaced, a pull up / pull down resistance is needed to keep the input at a defined logic. 4. Basic Digital Circuits ¶ Digital circuits are compositions of logic gates. A small number of digital circuits occur frequently in larger digital designs, such as
1. Pull-up and pull-down resistors
The inverse of pull up and pull down resistances are called output high drive and output low drive of the cell respectively. In general, cells are designed to have similar drive strength of pull up and pull down structures to have comparable rise and fall time. Combining these constructions we can get some complex structures. When connecting pull-up and pull-down network, they both try to make an output. The possible results are shown in Table 1. Here, high impedance (or Z floating) is possible as an output if pull-up and pull-down networks are both OFF. BASIC IDEAL SWITCH • Simplest structure in a computing system is a switch
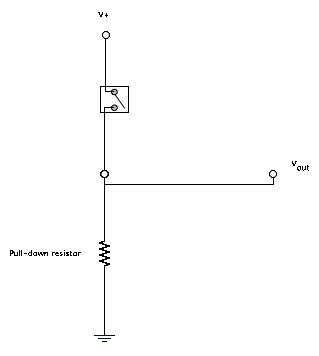
What Are Pull-down Resistors? Pull-down resistors work in the same manner as pull-up resistors, except that they pull the pin to a logical low value. They are connected between ground and the appropriate pin on a device. An example of a pull-down resistor in a digital circuit can be seen in the following figure. 17. It is also called as Differential Cascode Voltage Switch Logic (DCVSL). CVSL seeks the performance of pseudo NMOS without the static power
CMOS Gates: Pull Up Network Design In designing the pull-up network, see when the output ought to be HIGH and then arrange the PFETs accordingly. The pull-down network will have the complimentary topology. If either A or B is LOW, output will be If Digital circuits use microcontrollers, sensors, and other components to process inputs and outputs. Floating inputs can cause erratic behavior, but pull-up and pull-down resistors ensure stable logic levels and circuit reliability.This article explains their function, importance, selection, common mistakes, and advanced applications, providing a clear understanding of their role in
Features of GPIO Output states supports push-pull or open-drain + pull-up/down. Speed selection for each I/O. Input states can be configured as floating, pull-up/down, analog Locking mechanism (GPIOx_LCKR) is provided to freeze the port A or B I/O port configuration. The flexibility of selecting alternate functionality.
- Why NAND structures are preferred over NOR ones?
- 4. Basic Digital Circuits — Introduction to Digital Circuits
- Why Are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Used?
- Basics of SoC I/O design: Part 1
CMOS Digital Logic Circuits
Pull up resistors pull up a pin to a HIGH state. Pull down resistors pull down a pin to a LOW state. Therefore, we have well-defined pins. When pins are well What are pull-down resistors? Pull-down resistors work in the same manner as pull-up resistors, except that they pull the pin to a logical low value. They are connected between ground and the appropriate pin on a device. An example of a pull-down resistor in a digital circuit can be seen in the figure. A pushbutton switch is connected between the supply voltage and a microcontroller
Discover the purpose of pull-up and pull-down resistors in electronics. This article explains how these resistors stabilize input signals, prevent floating states, and ensure reliable logic levels in circuits, making them essential components in digital design. Full complementary gates can be designed as ratioless circuits: A fixed ratio in size between pull-up and pull-down structures is not required for proper operation.
A level shifter circuit is used to convert signals from one voltage level to another while maintaining the shape of the signal. This is commonly needed when interfacing different parts of a system that operate at different voltage levels, such as between microcontrollers, sensors, or other integrated circuits.
Introduction The STM32 microcontroller general-purpose input/output pin (GPIO) provides many ways to interface with external circuits within an application framework. This application note provides basic information about GPIO configurations as well as guidelines for hardware and software developers to optimize the power performance of their STM32 32-bit Arm® Cortex®
Combinational MOS Logic Circuits
pull-up device, which is typically either a bipolar junction transistor or an enhancement mode field effect transistor, and a pull-down device, which might be another transistor, or a resistor, current source, diode, etc. The stage load which is shown in the figure represents the input resistance of the following stage, which is typically a stage (or n stages) just like the original stage.
Basic Electrical Properties of MOS Transistor: IDS – VDS relationships, MOS transistor Threshold Voltage-VT, figure of merit-ω0, Transconductance- gm, gds; Pass transistor, NMOS Inverter, Pull-up to pull-down ratio of NMOS Inverter driven by another NMOS inverter (Z=4:1), Various pull ups, CMOS Inverter analysis and design. The pull-down network composed of nMOS transistors connected to ground, so that the circuit will conduct. These two pull-up and pull-down networks will turn on and off alternatively, depending on the input variables of the logic function.
- Cinnamon Sugar Mini Donuts Single Serve
- Chubby Boys Photos And Premium High Res Pictures
- Cientistas Identificam ‘Berçário De Estrelas’ Na Via Láctea
- Cinderella Light Blue Dress , Cinderella Light up Dress Toddler
- Citizen Eco-Drive Watch – Citizen Eco Drive One Angebote
- Cinco Siglos De Lexicografía ·Del Español
- Cities And Communes In Bayreuth
- City Cafe Am Rathaus : Böckeler´s Cafe am Rathaus GmbH
- City Of Detroit Celebrating 3,000 Demolitions Under
- Chunky Sneaker In Rosa – Sneaker-Trends 2025: Die Must-Haves für dein Schuhregal
- Chuyện Gì Đã Xảy Ra Trong Shutter Island
- Chronologie Des Régimes Politiques En France Depuis 1789
- Ciao Italia Pirque, Pirque | Ciao Italia Pirque, Pirque
- Cicaplast B5 Balzsam Spf50 : Cicaplast balzsam b5 spf 50
- Circumference Of A 12 Inch Diameter Circle