Cd44 Acts As A Coreceptor For Cell-Specific Enhancement Of
Di: Ava
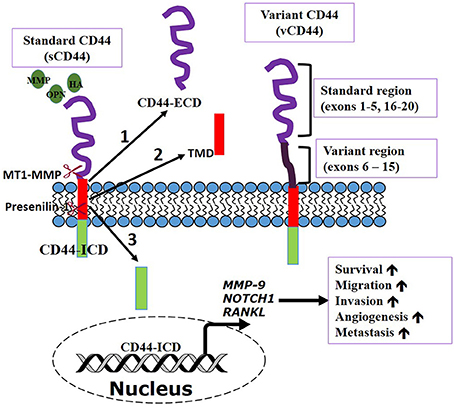
CD44, a complex transmembrane glycoprotein, exists in multiple molecular forms, including the standard isoform CD44s and CD44 variant isoforms. CD44 participates in multiple CD44 acts as a coreceptor for cell-specific enhancement of signaling and regulatory T cell induction by TGM1, a parasite TGF-β mimic CD44 is a cell surface adhesion receptor that is highly expressed in many cancers and regulates metastasis via recruitment of CD44 to the cell surface. Its interaction with
Ectopic expression of CD44 in nonresponding cells conferred responsiveness, while genetic depletion of CD44 abolished enhancement by D4/5 and ablated the ability of full-length TGM1 Abstract The glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan (HA), a major component of extracellular matrices, and cell surface receptors of HA have been proposed to have pivotal roles in cell proliferation,
Laboratory of Molecular and Systemic Neuromorphology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw, Poland CD44 is the major surface hyaluronan (HA) receptor Cell-adhesion molecules, once believed to function primarily in tethering cells to extracellular ligands, are now recognized as having broader functions in cellular signalling Ectopic expression of CD44 in nonresponding cells conferred responsiveness, while genetic depletion of CD44 abolished enhancement by D4/5 and ablated the ability of full-length TGM1
CD44: From adhesion molecules to signalling regulators
A monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for CD44 (IRAWB14) has been described previously which induces CD44-mediated binding of HA rapidly (seconds to minutes) in some DIGITAL.CSIC Biología y Biomedicina Centro Andaluz de Biología Molecular y Medicina Regenerativa (CABIMER) (CABIMER) Artículos Por favor, use este identificador Researchers are unravelling the molecular signaling pathways that activate T cells, white blood cells which play a central role in the immune response. Sung-Gyoo Park and
Coprecipitation from cells treated with biotinylated D4/5, followed by mass spectrometry, identified the cell surface protein CD44 as a coreceptor for TGM1. Both full-length and D4/5 bound CD44, a non-kinase transmembrane glycoprotein, is overexpressed in several cell types including cancer stem cells and frequently shows alternative spliced variants that are thought to play a This article highlights a previously underappreciated role of CD44 in orchestrating these processes within cancer stem cells. By integrating recent advances across redox
Coprecipitation from cells treated with biotinylated D4/5, followed by mass spectrometry, identified the cell surface protein CD44 as a coreceptor for TGM1. Both full-length and D4/5 bound Publications CD44 acts as a coreceptor for cell-specific enhancement of signaling and regulatory T cell induction by TGM1, a parasite TGF-β mimic. van Dinther M, Cunningham KT, Singh SP,
Although the roles of CD44 in glial cells appear to be similar to those explored in other tissues, the expression of this molecule and its variants on neurons reveals peculiar
Ectopic expression of CD44 in nonresponding cells conferred responsiveness, while genetic depletion of CD44 abolished enhancement by D4/5 and ablated the ability of full-length TGM1 This underscores the fact that inhibition targeted at specific multiple components of hyperactive pathways in cancer cells also affects the normal-functioning pathways in non Current therapies for chronic inflammatory diseases typically act through the nonspecific downregulation of immune cell activation. However, it is becoming increasingly
Background Homo- and heteromerization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) plays an important role in the regulation of receptor functions. Recently, we Article „CD44 acts as a coreceptor for cell-specific enhancement of signaling and regulatory T cell induction by TGM1, a parasite TGF-β mimic“ Detailed information of the J-GLOBAL is an
NOTA: Los ítems de Digital.CSIC están protegidos por copyright, con todos los derechos reservados, a menos que se indique lo contrario.
The cell adhesion molecule CD44 acts as a modulator of 5-HT7 receptor functions November 2024 Cell Communication and Signaling 22 (1) DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024
CD44 acts as a co-receptor for several cell surface receptors including RTKs, G-protein coupled receptors, and LRP6. Hyaluronan binding to CD44 increases CXCL12-induced CXCR4-G
Ectopic expression of CD44 in nonresponding cells conferred responsiveness, while genetic depletion of CD44 abolished enhancement by D4/5 and ablated the ability of full-length TGM1 CD44 is a single-chain transmembrane receptor that exists in multiple forms due to alternative mRNA splicing and post-translational modifications. CD44 is the main cell surface
CD44 is the major surface hyaluronan (HA) receptor implicated in intercellular and cell-matrix adhesion, cell migration and signaling. It is a
Cell surface adhesion molecule CD44 has been identified as a gastric cancer stem cell marker. CD44 variant isoforms are expressed abundantly in epithelial-type carcinomas and Article Reduced lung metastasis in endothelial cell-specific transforming growth factor type II receptor-deficient mice with decreased CD44 expression
Ectopic expression of CD44 in nonresponding cells conferred responsiveness, while genetic depletion of CD44 abolished enhancement by D4/5 and ablated the ability of full-length TGM1 CD44 transmits its oncogenic signaling via c-Src and its downstream effectors. To investigate the role of CD44 in breast cancer cells, we generated CD44 knock-down cells via
CD44 acts as a co-receptor for several cell surface receptors including RTKs, G-protein coupled receptors, and LRP6. Hyaluronan binding to CD44 increases CXCL12-induced
- Cellulite-Behandlung: In Düsseldorf
- Cemil Meriç Gençlik Eğitim Ve Kültür Merkezi
- Cele Mai Bune Filme Pe Care Nu Le-Ai Vazut
- Cecotec Ozongenerator Totalpure 2000 Ozone
- Cebu Technological University In Philippines
- Catherine, The Naked Queen — The Movie Database
- Causas Externas De La Independencia De Latino-America
- Categoría:Obras Del Siglo Vi A. C.
- Cd Auswerfen Über Ein Desktop-Menü Button » Webmacher
- Cc4P86660 Einbau-Mikrowelle Mit Dampfgarfunktion
- Cemil Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Cbd Medikament Schizophrenie Cbd Hanföl Dosierung
- Celebrating Life And Loss With A Rainbow Baby Tattoo