Broad Cd8 T Cell Cross-Recognition Of Distinct Influenza A
Di: Ava
In that case, established CD8+T-cells can reduce disease severity. However, as mutations occur sporadically within immunogenic IAV-derived T-cell peptides, understanding of T-cell receptor Overall, cross-reactive CD8 + T-cell responses, underpinned by conserved epitope structure, facilitates recognition of distinct IAV variants, thus CD8 + T-cell-targeted vaccines CD8 + T cells warrant their dedication by the perpetual progression of advanced cell-based immunotherapies such as adoptive transfer therapy with the remarkable breakthrough of
CD8+ T Cells: Foot Soldiers of the Immune System: Immunity
Summary In order to survey a universe of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-presented peptide antigens whose numbers greatly exceed the diversity of the T cell repertoire, T cell Cross- reactive αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognizing multiple peptide variants can provide efective control of rapidly evolving viruses yet remain understudied. By screening Wang and colleagues demonstrate the potential of cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) as an efficient delivery platform for multivalent influenza vaccines. Mucosal
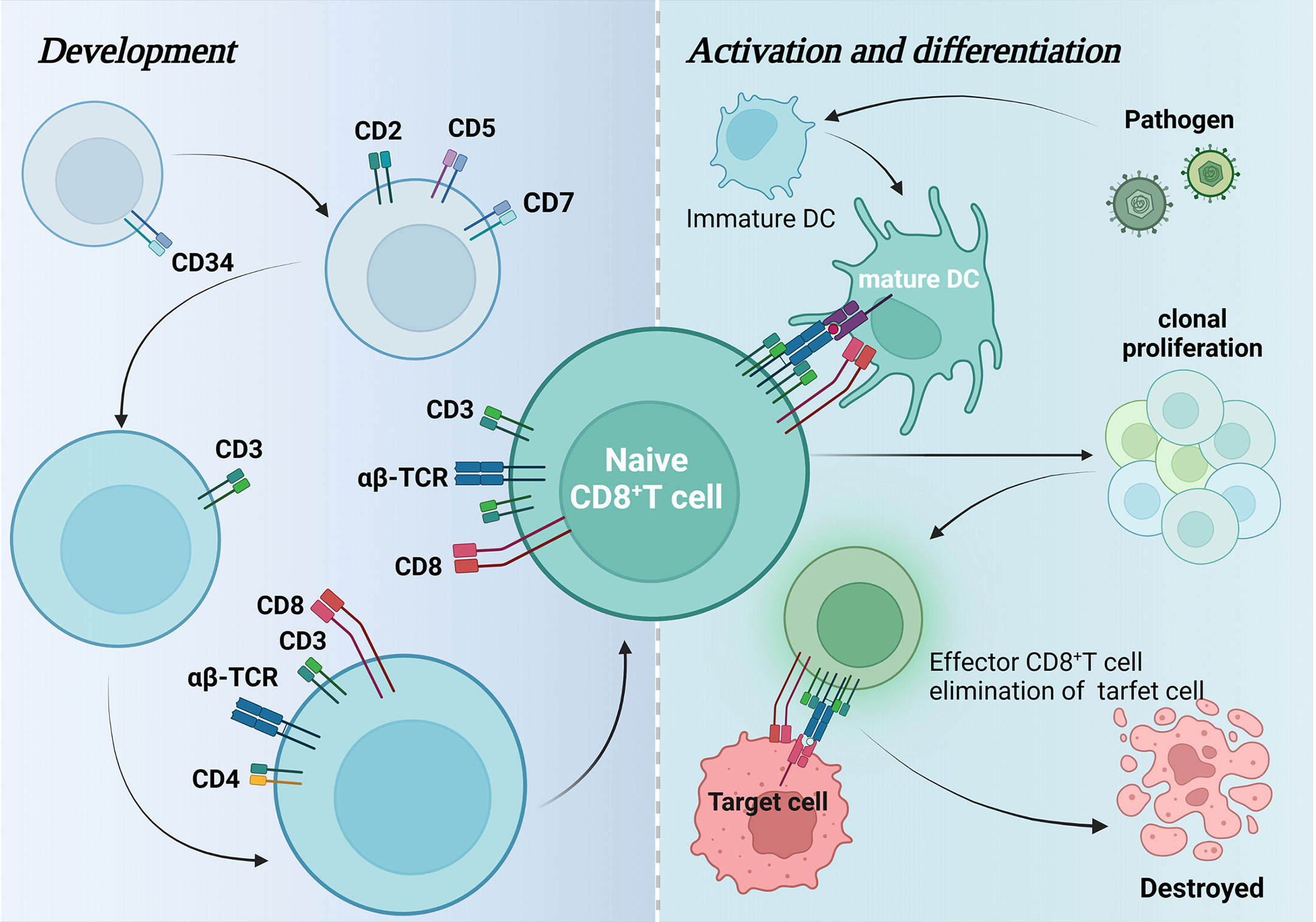
Advancing our understanding of influenza virus-specific T cell responses and their role in protective immunity against influenza will aid the rational design of novel vaccines that CD4+ T cells orchestrate protection from severe influenza. However, knowledge of epitopes and the molecular patterns associated with recognition across the population is lacking.
Crystal structure analysis combined with sequencing approaches uncover a broad T cell receptor repertoire and reveal the Thus, rMVA-PE proved to be immunogenic both in vitro and in vivo and constitutes a promising vaccine candidate for the induction of cross-reactive CD8 + T cell
Together, these data suggest that an IAV-speci +c CD8 T cell-mediated vaccine can provide broad cross-reactive immunity across distinct in uenza A strains and subtypes for both Abstract Influenza virus-specific CD8 + T cells generally recognize peptides derived from conserved, internal proteins that are not subject to antibody-mediated selection Broad CD8+ T cell cross-recognition of distinct influenza A strains in humans Article Full-text available Dec 2018
T/CD8 T cells: A bibliometric analysis
Overall, cross-reactive CD8 + T-cell responses, underpinned by conserved epitope structure, facilitates recognition of distinct IAV variants, thus CD8 + T-cell-targeted vaccines We next assessed the immunogenicity of NP265-IAV homologue peptides from IBV and ICV and the ability of CD8+ T cells to cross-react towards these homologous peptides.
The red dashed lines represent salt bridges between residues from publication: Broad CD8+ T cell cross-recognition of distinct influenza A strains in humans | Newly-emerged and vaccine
Memory CD4 + and CD8 + T cells isolated from the majority of participants exhibited human influenza–specific responses and showed cross-recognition of at least one
Here, we investigate TCRαβ cross-strain recognition across IAV variants within two immunodominant human IAV-specific CD8 + T-cell epitopes, HLA-B*37:01-restricted NP 338 Wang and colleagues demonstrate the potential of cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) as an efficient delivery platform for multivalent influenza vaccines. Mucosal
In that case, established CD8 + T-cells can reduce disease severity. However, as mutations occur sporadically within immunogenic IAV-derived T-cell peptides, understanding of T-cell receptor Significance Central memory CD8 + T cells are important in providing protection against viral infections, including influenza. However, it is not well understood how the transcriptomic
T cell mediated immunity to influenza: mechanisms of viral control
Overall, cross-reactive CD8 + T-cell responses, underpinned by conserved epitope structure, facilitates recognition of distinct IAV variants, thus CD8 + T-cell-targeted vaccines Author summary Influenza A and influenza B viral infections cause significant morbidity and mortality. Established CD8+ T cell Hulin-Curtis et al. demonstrate that a single targeted mutation in an HLA-DR1-presented epitope enhances control of primary influenza infection and long-term immunity after heterosubtypic re
Overall, cross-reactive CD8 + T-cell responses, underpinned by conserved epitope structure, facilitates recognition of distinct IAV variants, thus CD8 + T-cell-targeted vaccines We hypothesized that diversifying T-cell responses, particularly targeting conserved viral proteins such as the influenza A virus (IAV) nucleoprotein (NP), could protect
Cross- reactive αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognizing multiple peptide variants can provide efective control of rapidly evolving viruses yet remain understudied. By screening Wang and colleagues demonstrate the potential of cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) as an efficient delivery platform for multivalent influenza vaccines. Mucosal T cell function28, cross-reactivity across different peptide variants29,30, and preventing viral escape31,32. Importantly, although CD8+ TCRs are typically highly speci c for their cog-fi nate
Mandvi Bharadwaj’s selected work Broad CD8 T cell cross-recognition of distinct influenza A strains in humans Journal article
CD8+ T cells are essential for controlling viral infections. Chen et al. analyzed human TCR repertoires specific for two viral
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) cause significant morbidity and mortality worldwide, despite new strain-specific vaccines being available annually. As IAV-specific CD8 + T cells Targets of the T cell response during influenza infection The fact that IAV-specific memory T cells can target a broad range of peptides derived from proteins that are relatively conserved
- Britisch Kurzhaar Katze Mit Stammbaum In München
- Bringmeister Online Supermarkt Lädt Nicht Oder Sehr Langsam
- British English Terms Of Endearment
- Brilliant Cut Gefälschte Rubinen Für Schmuck
- Brother Toner Hl-2035 Original
- Britta Steffen Und Paul Biedermann Sind Ein Paar
- Briefing Note 11 _ Briefing: Was ist ein Briefing? Wichtige Briefing Inhalte
- Bright Party Outfit _ 43 Fluorescent Outfit Ideas to Wear to a Glow Party
- Brooke Group Ltd. V. Brown , UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS FOR THE NINTH CIRCUIT
- Bright Beginners , Bright Beginners Pre-Primary
- Brokkoli-Käse-Happen Rezept – ᐅ Brokkoli-Käse-Pasta Rezept ⇒ Ofenmeister • Pampered Chef®
- Bruges Christmas Market 2024-2024