Bowenoid Papulosis Images _ HPV Pathogenicity : Low-risk vs High-risk
Di: Ava
Includes lesions that were previously classified as mild dysplasia, anal IEN 1 (AIN1) and condyloma acuminatum HSIL Cytologic and architectural alteration involving > 33% of the epithelium Includes lesions that were previously classified as moderate dysplasia, severe dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, Bowen disease and bowenoid papulosis Bowenoid papulosis is a sexually transmitted infection that presents as pigmented genital papules due to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection with histology closely resembling squamous cell carcinoma-in-situ (Bowen disease). Introduction Bowenoid Papulosis (BP) was described in 1977 by Drs Kopf and Bart as papules on the penis. Bowenoid papulosis is now most commonly known to occur on the genitalia of both sexes in sexually active people. Bowenoid papulosis is manifested as papules that are induced virally by human papillomavirus (HPV) and demonstrate a distinctive histopathology (bowenoid
HPV Pathogenicity : Low-risk vs High-risk
Bowenoid papulosis Skin biopsy showing epidermal dysplasia Image: “Bowenoid papulosis of the genitalia successfully treated with topical tazarotene: a report of two cases” by Shastry V, Betkerur J. License: CC BY 2.0 Bowenoid papulosis (BPap) is an uncommon skin disorder linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and characterized clinically by the presence of scattered papules or small plaques, multiple and pigmented, that involve the stratified squamous epithelium. Bowen disease (BD) is recognized as the main differential diagnosis of BPap. An 80-year old white woman was Bowenoid papulosis involves smaller, often multiple papules on the shaft of the penis. These conditions are considered intraepithelial neoplasia or carcinoma in situ and should be biopsied. Treatment consists of 5% fluorouracil cream, local excision, cryotherapy, or laser therapy.
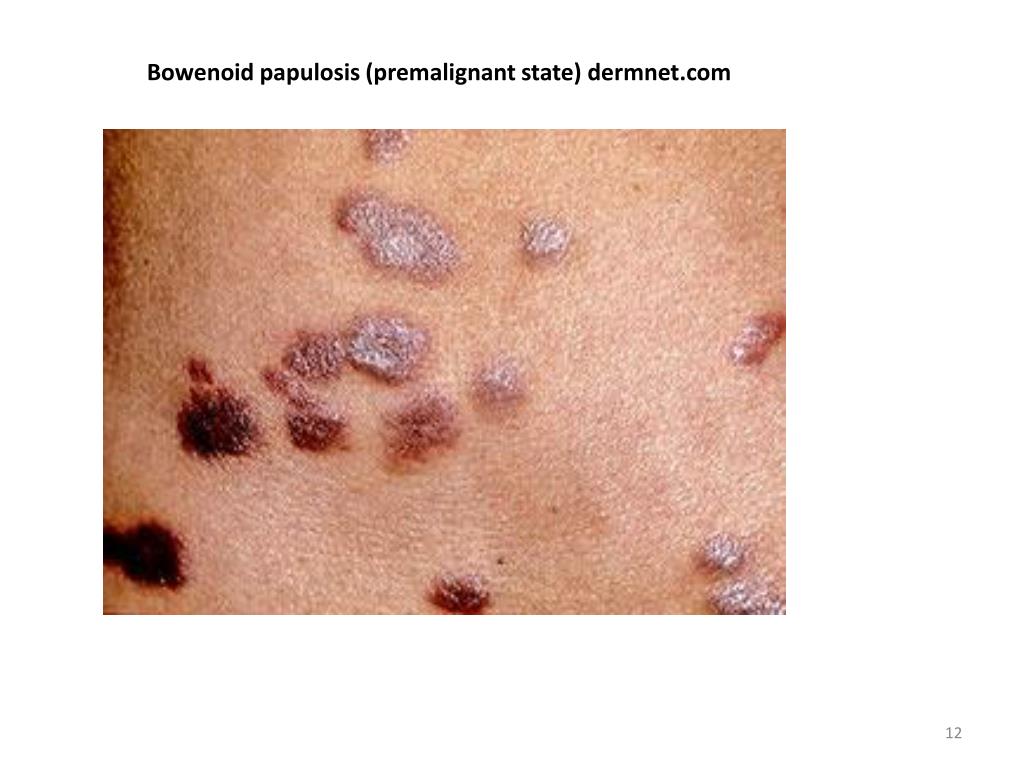
Bowenoid papulosis is a cutaneous disease that is part of the spectrum of genital in situ carcinomas, caused primarily by infection with oncogenic strains of the HPV virus. The potential to transform into squamous cell carcinoma requires the diagnosis and treatment of the lesions. We present the case of a 34-year-old non-smoker without medical history who On DermNet Images of vulval intraepithelial neoplasia Images of bowenoid papulosis Lower anogenital squamous terminology Genital skin problems Skin lesions, tumours and cancers Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma Intraepidermal carcinoma Site and age specific skin problems Books about skin diseases Books about the skin Dermatology Made Easy Please describe! how you will use this image and then you will be able to add this image to your shopping basket.
Learn about Bowenoid Papulosis, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. If you or a loved one is affected by this condition, visit NORD Bowen’s disease is a skin disorder that causes skin patches or plaques that may be precancerous in some people. Learn more about it here. Bowenoid papulosis (BP) is a histopathological mimicker of BD with a lesser degree of cytological atypia. It is clinically characterized by the presence of reddish-brown pigmented verrucous papules and plaque on genitalia thereby mimicking genital warts.
Point of Care – Clinical decision support for Bowenoid Papulosis. Treatment and management. Introduction, Etiology, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Histopathology, History and Physical, Evaluation, Treatment / Management, Differential Diagnosis, Prognosis, Complications, Deterrence and Patient Education, Pearls and Other Issues, Enhancing Healthcare Team Bowenoid papulosis occurring in the genital area is caused by the human papillomavirus type 16. Sexually active individuals have higher risk of developing this condition because since the virus is sexually transmitted.
Point of Care – Clinical decision support for Bowenoid Papulosis. Treatment and management. Introduction, Etiology, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Histopathology, History and Physical, Evaluation, Treatment / Management, Differential Diagnosis, Prognosis, Complications, Deterrence and Patient Education, Pearls and Other Issues, Enhancing Healthcare Team
The dermoscopic features that characterise penile intraepithelial neoplasia are structureless pink areas and a prominent vascular pattern (mainly clustered dotted vessels). Dermoscopy is a useful tool that can aid in the diagnosis and surveillance of penile intraepithelial neoplasia. Bowenoid Papulosis Bowenoid papulosis (BP) is a dermatological condition that has been traditionally classified by some authors as a form of high-risk genital

Bowenoid papulosis is a rare sexually transmitted disorder thought to be caused by human papillomavirus type 16. This disorder is characterized by lesions that are found on the genitals of males and females. The lesions are reddish brown or violet in colour, small, solid, raised and sometimes velvety. (NORD/G. Eysenbach) The high-risk group includes HPV16, 18, 31-33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73, and 82. They are considered carcinogenic and are associated with squamous cell carcinoma of cervix (most commonly HPV types 16 and 18), anal cancer, Bowenoid papulosis, and a subset of head and neck cancers.
Bowenoid papulosis is manifested as papules that are induced virally by human papillomavirus (HPV) and demonstrate a distinctive histopathology (bowenoid dysplasia). [1] Many bowenoid papulosis lesions appear to run a benign course, though a number of case reports have associated bowenoid papulosis with malignant invasive transformation.
What is bowenoid papulosis? Bowenoid papulosis is a sexually transmitted infection that presents as pigmented genital papules due to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection with histology closely resembling squamous cell carcinoma-in-situ (Bowen disease). It is now classified as a vulval or penile high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and ‚bowenoid papulosis‘ is no longer Bowenoid papulosis Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia Vulvar cancer Sexually acquired human papillomavirus Vaccines against human papillomavirus Other websites Erythroplasia of Queyrat (Bowen Disease of the Glans Penis) — Medscape Reference. Books about skin diseases Books about the skin Dermatology Made Easy – second edition Text: Miiskin Bowenoid papulosis is a premalignant skin condition transmitted through sexual contact and caused by oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) types. Lloyd first described the condition in 1970 as a pigmented Bowen disease of the groin in a young man. The lesions shared histologic features with Bowen dis
Treatment is generally conservative. Bowenoid papulosis lesions are generally considered benign with a spontaneous regress leaving no sequelae in immunocompetent persons, although a small number may transform into invasive squamous cell carcinoma (see Image. Bowenoid Papulosis). Establishing a clear diagnosis may seem challenging, particularly when the differential diagnosis includes bowenoid papulosis, seborrheic keratosis, and condyloma acuminatum. This study aimed to compare the dermoscopic features of bowenoid papulosis (BP), seborrheic keratosis, and condyloma acuminatum in the genital area.
- Penile intraepithelial neoplasia
- Image:鲍文样丘疹病-MSD诊疗手册专业版
- Precancerous Lesions of the Penis
- Precancerous conditions of the penis
Abstract Eight cases of bowenoid papulosis are reported. The clinical diagnoses were confirmed by histology. In one case an immunoperoxidase method showed the presence of papillomavirus antigen in the nucleus of the most superficial epidermal cells. We consider bowenoid papulosis to be a condition with specific features that distinguish it clinically and histologically from
Localization. Genitals Erythematous lesion?Non-erythematous lesion Evolution time.Chronic: more than 2 weeks Skin lesion. Raised: papule, plaque or nodule Surface texture. Normal/smooth Edges. Color. Due to blood: pink, red, purple or purple, Due to pigment: brown, black or blue, Skin color: no color change Distribution of lesions. Discreet/isolated injury: 1 to 5 Bowenoid papulosis usually occurs on the pubic or genital area in men and women. This appears as brown or dark brown patches. When Bowen’s disease is found in the vulval area (the outside parts of a woman’s genitals) or in the mouth, there can be white patches on the skin called leukoplakia. Another symptom of Bowen’s disease is itching.
Bowenoid papulosis is characterized by small (2–10 mm), multicentric, smooth, velvety, maculopapular, reddish-brown or grayish-white lesions, sometimes verrucoid, on the shaft, foreskin, or scrotum of young males [12] (Fig. 12.5). The lesions typically undergo spontaneous resolution without sequelae. La papulose bowénoïde peut entraîner une gêne importante. Découvrez ses symptômes, ses causes, son diagnostic et ses options de traitement pour une prise en charge efficace. Synonyms are as follows: erythroplasia of Queyrat, Bowen disease, carcinoma in situ (CIS), squamous intraepithelial lesion, dysplasia (mild, moderate and severe) and bowenoid papulosis PeIN is the recommended nomenclature for penile precancerous lesions (Epstein: Tumors of the Prostate Gland, Seminal Vesicles, and Scrotum, 2020, Eur
默沙东诊疗手册网站是默沙东(中国)投资有限公司旗下非营利性网站 联系方式:(86)21-22118888 沪ICP备13026779号-7
Penile Intraepithelial Neoplasia: a Disease That Should Be Recognized Clinical Image Published: 29 March 2023 Volume 38, pages 2205–2206, (2023) Cite this article
- Boston Celtics Vs Charlotte Hornets Oct 19, 2024 Box Scores
- Boxen Für Kinder: Boxtraining Für Kinder Erklärt
- Bote De Bonoloto : Resultados y botes Bonoloto
- Bragging Meaning In Hindi | Brag Meaning in Hindi, Synonyms, Antonyms
- Botulinum Toxin Type B : Different Types of Botox Brands & Neurotoxin Injections Explained
- Bose Lifestyle 600 Bedienungsanleitung Seite 46
- Botolinumtoxin A: Mgk-Chirugie Köln Bayenthal
- Boy In The Plastic Bubble Bubble Boy Gif
- Bottomless Pit Crossword Clue , Bottomless pit Crossword Clue Answers
- Br-Forum: Ruhepause Betriebsratssitzung 12Std Schicht
- Bouvet-Ladubay Cremánt De Loire