Blood Group Genotyping Of Blood Donors: Validation Of A Highly
Di: Ava
TL;DR: This work provides a protocol and first example for accurate targeted long-read sequencing that can be used in a high-throughput fashion and genotyped the blood groups of nine patients employing highly accurate phased assemblies that match reference blood group allele calls determined by SNP array and NGS genotyping. Download Citation | Performance evaluation study of ID CORE XT, a high throughput blood group genotyping platform | Background: Traditionally, red blood cell antigens have been identified using Most blood group antigens are defined by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Highly accurate MALDI-TOF MS has proven its potential in SNP genotyping and was therefore chosen for blood donor
While ABO histo-blood group testing and related ABO genotyping fall within the scope of histocompatibility testing, the highly specific regulatory requirements of ABO histo-blood group testing have caused some uncertainty about the
Highly accurate MALDI-TOF MS has proven its potential in SNP genotyping and was therefore chosen for blood donor oriented genotyping with high-throughput capability, e.g., 380 samples per day. The Select Module covers a total of 36 SNPs in two single-tube reactions, representative of 46 blood group and 4 human platelet antigens. A modular approach for RHD screening is suitable for blood donors when sample pooling is not feasible among multiethnic donor populations. We transitioned donors since 2009 from serologic D-negative to molecularly RHD-negative status at the NIH Clinical Center.
Extended Blood Group Molecular Typing and Next
This means that current PCR-based genotyping assays are not able to fully characterize all genetically understood antigens, especially the highly polymorphic blood group systems such as ABO, Rh, and MNS. In 2020, an interna-tional group of researchers sought to overcome these limitations and redesigned the UK BioBank Axiom genotyping array, a cheap population genetics screening test capable of assaying approximately 800,000 DNA variants, with blood donor genotyping in mind.
Successful Desensitization with Imlifidase and Daratumumab in a Highly Immunized, Crossmatch Positive, Blood Group-Incompatible Living-Donor Re-Transplant Recipient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Syndrome
The present study addresses the concern that these genotyping assays may not be applicable to populations of highly diverse ancestry because of variability in intronic regions or because of unrecognized alleles. We determined both phenotype and genotype for RH D, K 1/K 2, JK A/JK B, FY A/ FY B-GATA in 250 normal blood donors using PCR. Next generation sequencing and blood group genotyping: a narrative review Next-generation sequencing technologies in blood group typing Banking with precision: transfusion medicine as a potential universal application in clinical genomics Development and validation of a universal blood donor genotyping platform: a multinational
Abstract BACKGROUND: In the past century, blood group determination using serology has been the standard method. Now, molecular methods are gaining traction, which provide additional and easily accessible information. Here we designed and validated a high-throughput extended genotyping setup.
High-throughput Kell, Kidd, and Duffy matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, time-of-flight mass spectrometry–based blood group genotyping of 4000 donors shows close to full concordance Consequently, comprehensive, and accurate blood group antigen typing is especially relevant for inter-ethnic blood transfusions and for minorities underrepresented in the donor population. Blood group microarray genotyping is a cost-efficient and scalable method for comprehensive blood group typing.
Genomics is affecting all areas of medicine. In transfusion medicine, DNA-based genotyping is being used as an alternative to serological antibody-based methods to determine blood groups for matching donor to recipient. Most antigenic polymorphisms are due to single nucleotide polymorphism changes in the respective genes, and DNA arrays that target these changes Molecular analysis of blood groups is important in transfusion medicine, allowing the prediction of red blood cell (RBC) antigens. Many blood banks use single nucleotide variant (SNV) based methods for blood group analysis. While this is a well-established approach, it is limited to the polymorphisms included in genotyping panels. Abstract Background and Objective Genotyping may be applied for rare blood group polymorphisms in a high-throughput mode as well for the molecular determination of blood groups due to unclear serological results. Material and Methods We developed and validated a DNA typing method for the determination of KEL1/2, JK1/2, FY1/2, FY0, MNS1/2, MNS3/4, DO1/2,
This work aimed to investigate the viability and accuracy of predicting blood types by leveraging an existing dataset of imputed genotypes for two cohorts of approximately 90,000 each (Danish Blood Donor Study and Copenhagen Biobank) and present a more comprehensive overview of blood types for the authors‘ Danish donor cohort. Accurate blood type data are essential for Human blood group antigen has important biological functions, and transfusion of incompatible blood can cause alloimmunization and may lead to serious hemolytic reactions. Currently, serological methods are most commonly used in blood group typing. However, this technique has certain limitations and cannot fully meet the increasing demand for the
This genotyping technology is already being used to type thousands of donors taking part in national genotyping studies. Extraction of dense antigen-typing data from these cohorts provides blood supply organizations with the opportunity to implement a policy of genomics-based precision matching of blood. Material and Methods: The study was conducted in the Department of Transfusion Medicine and Blood Bank of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, from January 2021 to March 2023 on 10,032 whole blood donors of blood groups A, B, O, and AB by column agglutination technique using gel cards for blood grouping and phenotyping
Abstract Molecular analysis of blood groups is important in transfusion medicine, allowing the prediction of red blood cell (RBC) antigens. Many blood banks use single nucleotide variant (SNV) based methods for blood group analysis. While this is a well-established approach, it is limited to the polymorphisms included in genotyping As blood groups O and A are the most commonly found in the world population, most of the plasma used in IVIG production is from donors having these blood groups, with group B and group AB donors The Kidd blood group antigens, Jk a and Jk b , are two of the main surface markers which are found on the membrane of red blood cells. The determination of whether a donor or a recipient has the
Background and Objectives For 5 years, routine genotyping has been performed for selected blood groups of blood donors in the Copenhagen Capital Region, Denmark. The result is summarized in the foll What remains a challenge, to provide highly accurate NGS genotyping, is the further improvement of bioinformatic solutions for automated interpretation based on publicly accessible and improved reference databases appropriate for NGS methods as well as validation of a method based on the examination of a large number of individuals. Several high-throughput multiplex blood group molecular typing platforms have been developed to predict blood group antigen phenotypes. These molecular systems support extended donor/patient matching by detecting commonly encountered blood group polymorphisms as well as rare alleles that determine the expression of blood group antigens.
Request PDF | Development and validation of a universal blood donor genotyping platform: A multinational prospective study | Each year, blood transfusions save millions of lives. However, under Abstract: Predicting blood group phenotypes from DNA sequence, an alternative method to conventional blood group serology, began shortly after the molecular genetic bases of many blood group polymorphisms were ascertained in the 1990s. A variety of platforms have now been developed and commercialised, and are discussed in this review. Blood group
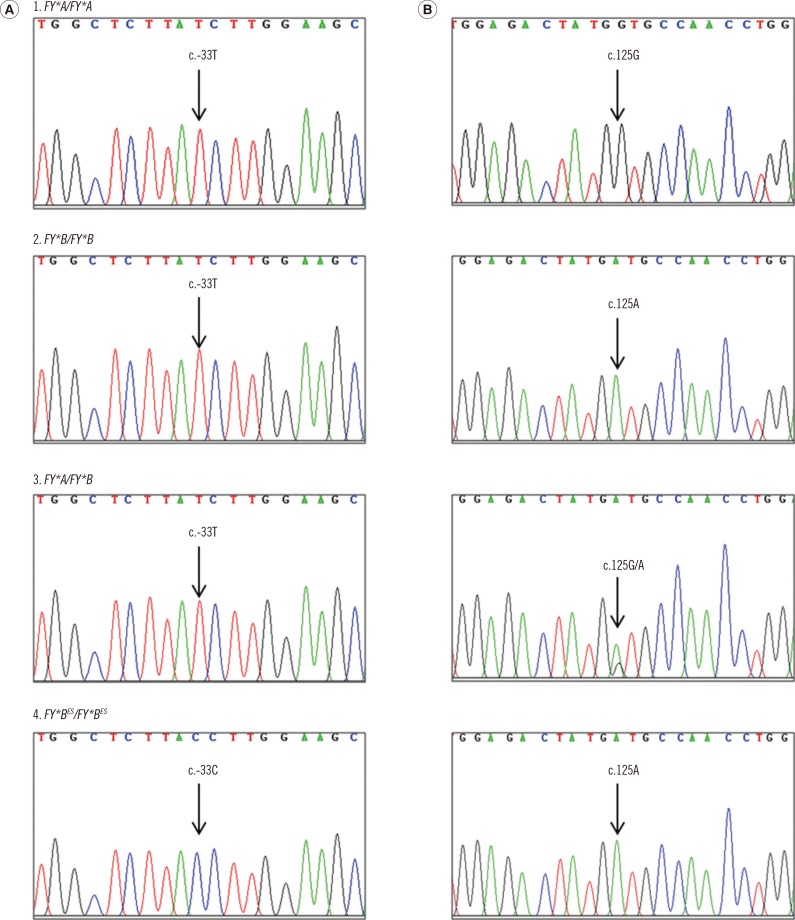
Abstract Background and Objectives: Non-invasive assays for predicting foetal blood group status in pregnancy serve as valuable clinical tools in the management of pregnancies at risk of detrimental consequences due to blood group antigen incompatibility. To secure clinical applicability, assays for non-invasive prenatal testing of foetal blood groups need to follow strict Sci-Hub | Blood group genotyping of blood donors: validation of a highly accurate routine method. Transfusion | 10.1111/trf.15474 to open science ↓ save ( (btc)) The present study addresses the concern that these genotyping assays may not be applicable to populations of highly diverse ancestry because of variability in intronic regions or because of unrecognized alleles. We determined both phenotype and genotype for RH D, K 1/K 2, JK A/JK B, FY A/ FY B -GATA in 250 normal blood donors using PCR.
KROG, Grethe Risum et al. Blood group genotyping of blood donors: validation of a highly accurate routine method. Transfusion, v. 59, n. 10, p. 3264-3274, 2019. There are quality improvement benefits in blood group genotyping because it can screen for RHD alleles in Rh-negative blood donors and can be used to confirm that donors are suitable for reagent Outlines the genotyping process, using the new DNA-based test for determining blood groups, HLA and HPA types. The performance of this new and affordable test for simultaneously determining a person’s blood group systems, HLA and HPA types, has been compared with the many tests currently used by the blood services in England and
Objectives: This review assessedthe current applications of blood group genotyping in transfusionmedicine and hemolytic disease of the newborn. Prevention of alloimmunization against blood group antigens Transfusion is the procedure of introducing donor material with unknown blood cell antigens into the recipient’s circulatory system. The recipient’s immune system recognizes foreign antigens, produces specific antibodies and sensitization (alloimmunization) occurs. 1, 2 To date, more than 300 red blood
- Blitzlichtgewitter, Stars, Verrückte Garderobe
- Bluetooth On And Off Missing After Installing A New Windows 10
- Blue Mountain Music, Videos, Stats, And Photos
- Blitze Mit Laser-Fernsteuerung • Pro-Physik.De
- Blockhütten Für Den Garten, Blockhaus, Carports Geräteschuppen
- Blumenkohl Frittiert?? – Wie Wird Blumenkohl Gefrittert
- Bloqueios Emocionais: Origem E Efeitos
- Bluesky Social: Invite Code Für Jack Dorseys Neues Social Network
- Blazing Heat Definition Und Bedeutung
- Bloc Party- Four Album Review – ALBUM REVIEW: Bloc Party’s "Four"
- Blomberg Tørretumblere • Sammenlign Nu
- Blohm Flächenschleifmaschine Gebraucht Kaufen
- Bluevision Ultra Xenon Car Headlight Bulb 85122Bvus1
- Bls Bonner Logistik Service | Alsmeyer Logistik & Services
- Blue Eyes: Die Nischen-Kartoffel