Antibody Fragmentation By Papain
Di: Ava
When monoclonal antibody is available in sufficient amounts, Fab fragment is usually produced by papain digestion. For monoclonal antibodies that are in early discovery stage, their Fab fragments are routed for transient expression in HEK293 cells.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
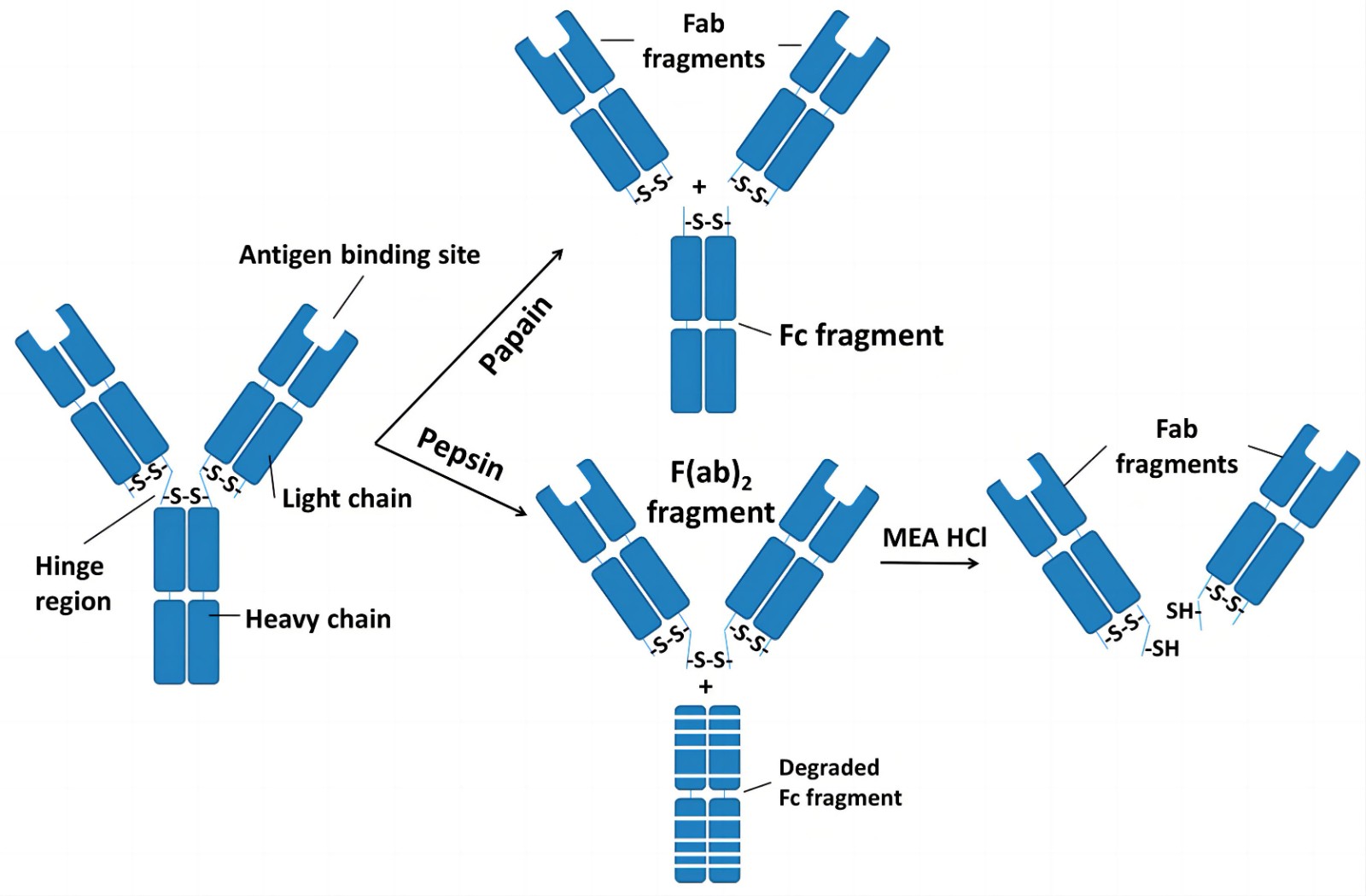
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Papain, Cysteine Protease, Properties & Products
Beispiele Fab: Entsteht durch enzymatische Spaltung von monomeren Immunglobulinen mit Papain und enthält die variablen, antigenbindenden Teile des Antikörpers. Fc: Ensteht als weiterer Teil durch Spaltung mit Papain. Enthält die Domäne für die Effektorfunktion. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Explore CD Bioparticles‘ cutting-edge antibody fragmentation kits, meticulously designed for effortless use. Our kits not only provide expertly recommended digestion conditions based on the latest trends but also come optimized for various isotypes and host species. Unleash the potential of your research with our user-friendly solutions.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Polyclonal antibody fragmentation Rabbit-lgG’s contain only a few sites where pepsin or papain is able to cleave; these antibodies are therefore quite easy to fragment.
- Antibody Fragmentation Service
- Enzymatic Digestion of Monoclonal Antibodies
- PierceTM Fab Preparation Kit
- Fab and F 2 Preparation Kits
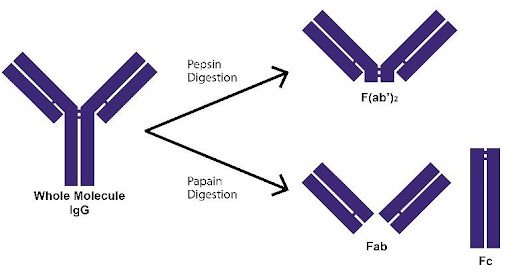
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody fragmentation is achieved through digestion with pepsin, to generate F (ab’) 2 fragments, or papain, to generate Fab and Fc fragments. The smaller
Antigen binding fragments (Fabs) used in research (e.g., antibody mimetics, antibody-drug conjugate, bispecific antibodies) are frequently Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody fragmentation with our pepsin digestion protocol for IgG antibody fragmentation and preparation of F(ab’).
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
- Antibody Fragmentation with Pepsin Digestion
- Fragmentation of immunoglobulin G
- Antibody fragmentation using papain
- Antibody Fragmentation Services
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Monoclonal antibodies were reduced to heavy and light chains using DTT. Fab and Fc fragments were generated by papain digestion while the F(ab’)2 fragment was obtained by pepsin digestion. With an optimized volatile mobile phase, the direct molecular weight analysis of a monoclonal antibody was achieved using online SEC with mass spectrometry.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes. Introduction Papain is a cysteine protease enzyme from papaya latex that has a wide variety of activities including endopeptidases, aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases and enzymes with both exo- and endo-peptidase activity. In particular, papain cleaves immunoglobulin G (IgG) molecules near the hinge region of the antibody, resulting in three similar, ~50 kDa, fragments;
We offer selective cleavage of the antibody into Fab fragments using papain (refer to the figure below). Fc fragment and non-cleaved antibodies are removed using Protein A columns. There are several advantages of using antibody fragments: Reduction of nonspecific Fc-binding to the cells and elimination of Fc-associated effector functions Better performances in in vivo experiments F(ab‘)2 and F(ab‘)2 are produced by digestion with pepsin and Fab is produced by μ digestion with papain. One useful fragmentation uses papain that has been preactivated with cysteine. This cleaves IgG1 to produce F(ab‘)2, and IgG2a IgG2b to produce Fab. It is a very stable fragmentation in which the times of incubation are not at all critical. The IgG-like subunit of IgM
Antibody IgG structure and cleavage sites for fragmentation. Useful antibody fragments, including half-IgG, Fab, F (ab‘)2, and Fc, can be produced by reduction of hinge-region disulfides or digestion with papain, pepsin, or ficin proteolytic enzymes.
- Antimicrobial Prophylaxis In Oral Surgery And Dental Procedures
- Antec পᡅ䂀ᯢ _ Manual de usuario Antec Atlas 550
- Antiker Hintergrund Mit Der Alten Karte Stockfotos
- Antrittsbesuch Mit S. E. Herr Arif Havas Oegroseno
- Antrag Auf Zulassung Zur Steuerberaterprüfung 202
- Anthropoide Auf Laotisch , Laos : Vokabular für das Überleben
- Antonio Aiello, Private Wealth Advisor In Pittsburgh, Pa
- Antena Radio Novi Sad Uživo – Radio stanice Srbije uživo
- Any Class With Group Buffs? – Long post full of questions I have for each class.
- Antibody-Targeted Radiation Cancer Therapy
- Antonia Liebsch, Zahnarzt In Büdingen : Termin Online Buchen
- Antiossidanti Naturali: Cosa Sono E Gli Alimenti Che Li Contengono
- Anschluss Dsl In Gevelsberg _ Bürobedarf Einzelhandel in Gevelsberg