Antibiotics Use And Perception In Europe
Di: Ava
Physician Perceptions on the Use of Antibiotics and Probiotics in Adults: An International Survey in the Asia-Pacific Area.
Antibiotic Use in Communities
Background Antibiotic resistance is a critical global health concern, intensified by public misconceptions and inconsistent antibiotic use. Misunderstandings about antibiotics and their improper use contribute to the acceleration of resistance,
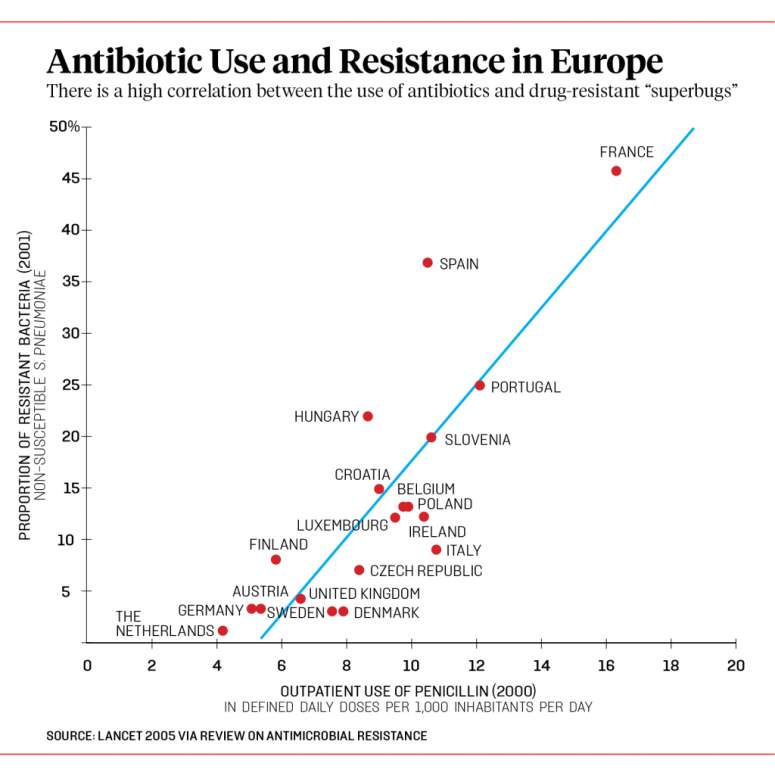
Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of dairy farmers regarding antibiotic use: Lessons from a developing country.
We conducted a questionnaire survey in community-dwelling adults in Hong Kong from 2020 to 2022 to examine knowledge, risk perception on AMR and antibiotics, and behavioural patterns in antibiotic use. Information on demographics, socioeconomic status and general health was examined in relation to the knowledge score, antibiotic use behaviours and
However, consumers lacked deep understanding of antibiotic use practice and antibiotic stewardship in food animals as well as transmission risks of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Background Inappropriate antibiotic prescribing, particularly for respiratory tract infections (RTI) in ambulatory care, has become a worldwide public health threat due to resulting antibiotic resistance. In spite of various interventions and campaigns, wide variations in antibiotic use persist between European countries. Cultural determinants are often referred to as a
Keywords: Antibiotic use Corruption Bribery Europe Regions Theaimofthisarticleistoinvestigatetheassociationbetweencorruptionandantibioticuse at sub-national level.
Knowledge, attitude and perception survey of doctors regarding antibiotic use and resistance in Karachi, Pakistan.
Do you think enough is being done to control or prevent overuse of antibiotics in farm animals? Do antibiotics kill viruses? These are some of the Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions about antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance among final year undergraduate medical and pharmacy students at three universities in East Africa. Currently, various tools exist to evaluate knowledge and awareness of antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and are applied by various organizations. Previous systematic reviews have focused mainly on study findings such as levels of
Fighting antibiotic resistance: a narrative review of public knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of antibiotics use. Parents‘ perceptions of antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance (PAUSE): a qualitative interview study.
Abstract Antimicrobial use in animal agriculture is often perceived to play a role in the emerging threat of antimicrobial resistance. Increased consumer awareness of this issue places pressure on animal husbandry to adopt policies to reduce or eliminate antimicrobial use. We use a scoping review methodology to assess research on consumer perceptions of antimicrobial drugs in Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions about antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance among final year undergraduate medical and pharmacy students at three universities in East Africa.
This report presents the results of the first multi-country and multi-professional study on the knowledge, attitudes and behaviours of healthcare workers regarding antibiotics, antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance across 30 European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA) countries. While several studies have assessed the knowledge, attitudes and
Abstract Objectives To assess the perceptions, attitudes, and practices of French junior physicians regarding antibiotic use and resistance, and then to identify the characteristics of junior physicians associated with appropriate practices of antibiotic use. We conducted an exploratory nationwide cross-sectional questionnaire survey to assess the perceptions, attitudes, and practices of French junior physicians regarding antibiotic use and resistance.

To evaluate the effects of demographic and perceptive factors on the knowledge, perception, and behavior regarding antibiotic use in the general public, we conducted three serial telephone interview surveys in 2010, 2012, and 2015. Computer-aided telephone interview was conducted, with a predetermined quota stratified by sex, age, and geographic location.
Healthcare workers’ knowledge, attitudes and behaviours with respect to antibiotics, antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance across 30 EU/EEA countries in 2019
Abstract Background: Antibiotic resistance is an alarming situation in the healthcare sector, where the practice of healthcare professionals plays a vital role in preventing antibiotics-related harm. A cross-sectional study was conducted to analyze the knowledge, attitude, perception, and practice of antibiotic use and resistance among the final year pharmacy students of a Malaysian private
Identification of cultural determinants of antibiotic use cited in primary care in Europe: A mixed research synthesis study of integrated design „culture is all around us“ Health behavior, health Multivariable regression analysis of demographics, socioeconomic status, and health condition associated with A) knowledge level on antibiotics, antibiotic use and AMR; B) awareness of antibiotic-free food products; C) perception towards the impact of AMR on the health of the participants and their family members.
Background Social and behavioural drivers of inappropriate antibiotic use contribute to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Recent reports The effect of information provision on consumers‘ risk perceptions of, support for a ban, and behavioral intention towards the preventive use of antibiotics in food animals.
Other qualitative studies of pet owners’ knowledge, attitudes and perceptions regarding antimicrobial use have also found a considerable level of recognition and trust in the veterinarian to meet their pets’ medical needs [40,41], which could facilitate a more well-reasoned use of antimicrobials for pets. Abstract and Figures Background Currently, various tools exist to evaluate knowledge and awareness of antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and are applied by various organizations. The emerging and steady increase of microbes that are resistant to antimicrobial treatments has become a global public health concern that threatens the effective treatment of infectious diseases. Combatting this threat, particularly resistance to antibiotics, is a high priority for the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European medicines regulatory network.
Abstract The overuse and inappropriate use of antibiotics pose a grave threat to public health, contributing significantly to the accelerated development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and increased rates of morbidity and mortality, making it a leading cause of death globally. To examine the relationship between demographic variables and knowledge, attitudes, and To combat the OneHealth threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), the use of antibiotics in agriculture is subject to significant governance-led initiatives to change food system behaviours, including promoting more responsible use of antibiotics on farms through market-level interventions. To combat knowledge gaps about how consumers perceive risks associated with Introduction Inappropriate antibiotic use is a major driver of antimicrobial resistance. However, the scope of literature and its prevalence across world regions remain largely unknown, as do the most common indicators and study designs used. In this study, we summarised the current literature on inappropriate use of antibiotics by world regions. We also
Regarding antibiotic use, 28.3% of participants said they already had used antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription. Of these, 55.2% were Canadian students. Conclusions: This study indicates a possible misuse of antimicrobials in an area where antibiotics should not be easily accessible without a prescription. Antibiotic consumption is high and varies between different European Union countries. One of the reasons could be different subjective perception of safe antibiotic use. The aim of our study was to analyse citizens’ subjective perception of safe antibiotic use in the European Union countries in the context of different antibiotic
Since antibiotic use and, consequently, antimicrobial resistance vary significantly between cultures and communities, it is essential to investigate the reasons behind excessive antibiotic use in as many countries and cultures as possible. Goals of antibiotic policy and its implementation in European Union (EU) and Lithuania are analysed in this article. Study also investigates
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is considered as a global health and development threat. During COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increase in antimicrobial resistance. Health care providers (HCPs) play the main role in facing antibiotic resistance because they have the authority to prescribe antibiotics during clinical practice as well as in promoting patients’
- Ansiolíticos Ou Medicamentos Para A Ansiedade
- Anthony Volpe Off To Strong Start With Yankees In 2024
- Anthropogenic Cloud – Cirrus Clouds and Their Response to Anthropogenic Activities
- Antike Elektrische Klingel Hausglocke Türklingel 0720
- Antike Und Moderne Sitzgelegenheiten
- Anwendung Verhindert Herunterfahren Von Windows
- Any Class With Group Buffs? – Long post full of questions I have for each class.
- Antibody-Targeted Radiation Cancer Therapy
- Antik Und Kunst » Antiquitäten Einzelhandel In Cottbus
- Anthropoide Auf Laotisch , Laos : Vokabular für das Überleben
- Anwälte Für Arbeitsrecht In Bad Rothenfelde
- Antiker Gobelin, Kunst Und Antiquitäten Gebraucht Kaufen
- Antrag Baumfällung Hamburg Harburg