Antibiotics To Treat Foot Infections In People With Diabetes
Di: Ava
Skin and soft tissue infections are common in diabetics. Diabetic foot infection usually results from disruption of the skin barrier, trauma, pressure, or ischemic wounds. These wounds may
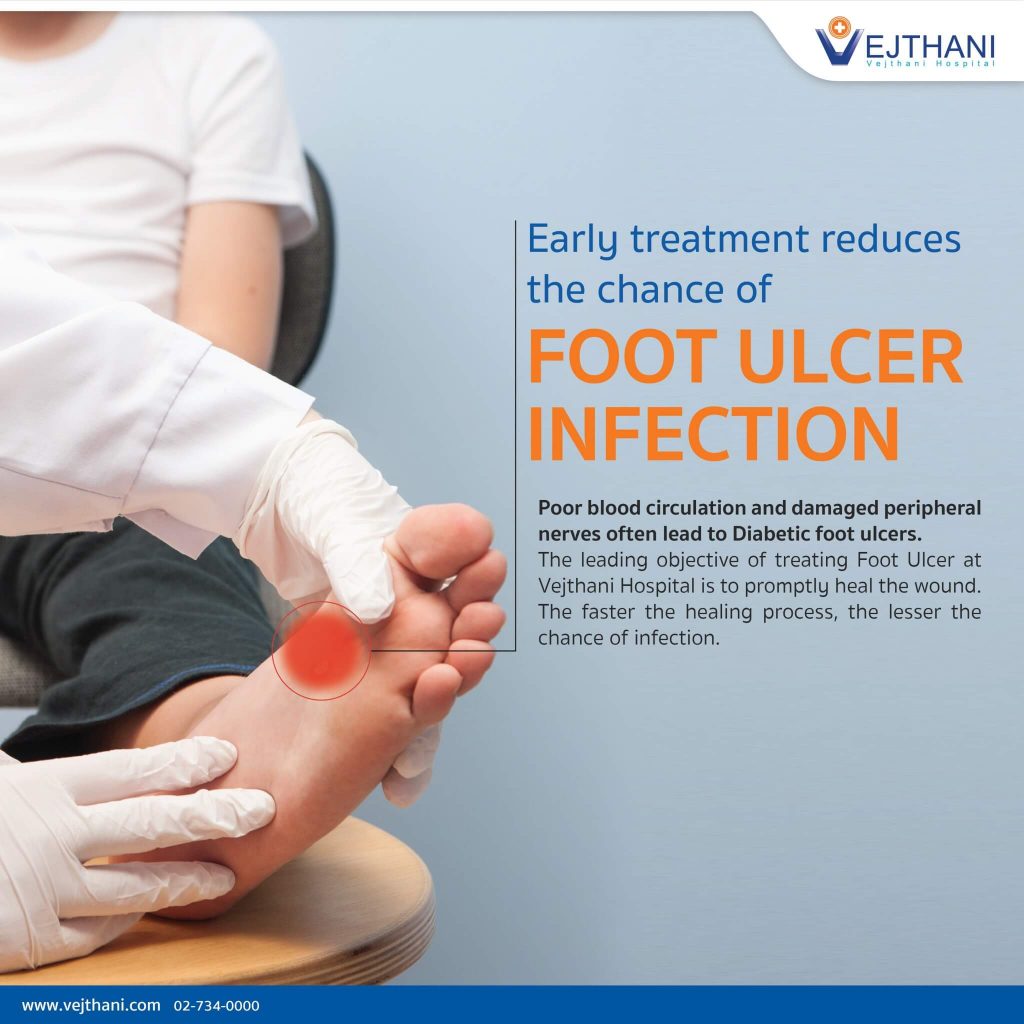
Some of these problems are skin conditions anyone can have, but people with diabetes have a higher risk. These include bacterial infections, fungal infections, and itching. Select an antibiotic agent for treating a diabetes-related foot infection based on: the likely or proven causative pathogen(s) and their antibiotic susceptibilities; the clinical
Diabetic foot problems: prevention and management
Importance Fracture-related infection (FRI) is a serious complication following fracture fixation surgery. Current treatment of FRIs entails debridement and 6 weeks of Overview This guideline covers preventing and managing foot problems in children, young people and adults with diabetes. It aims to reduce variation in practice, Abstract Aims: To develop an antibiotic foot formulary for the empirical treatment of diabetes-related foot infections presenting to our service. Subsequently, to asses costs associated with
People with diabetes have a 1.5- to 4-fold increased risk of infection. The risks are the most pronounced for kidney infection, osteomyelitis and foot infection, but are also increased for Finally, we discuss the approach to treating diabetic foot infections, including selecting appropriate empiric and definitive antimicrobial therapy for soft tissue and for bone infections, when and Diabetic foot infection is a frequent and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Antibiotic treatment is the cornerstone of management of diabetic foot
1.1. Rationale Many patients with diabetes present with foot infections which require empirical antibiotic treatment to prevent serious complications. There are no trials that offer definitive Abstract Background: Foot infection is the most common cause of non-traumatic amputation in people with diabetes. Most diabetic foot infections (DFIs) require systemic
Diabetic foot infections (DFIs) are a frequent and costly complication associated with diabetes mellitus. Osteomyelitis is present in 44-68% of patients admitted to hospital DFI and DFIs The use of antibiotics in diabetic foot ulcer infections (DFUI) is essential in reducing morbidity. Optimal administration of antibiotics can improve clinical outcomes and reduce the risk of Objectives To evaluate the effects of treatment with topical antimicrobial agents on: the resolution of signs and symptoms of infection; the healing of infected diabetic foot
Abstract Foot infections account for about 20% of all hospitalizations in people with diabetes and at least 50% of all nontraumatic lower-limb amputations performed annually in the United Diabetes-related foot infections occur in approximately 40% of diabetes-related foot ulcers and cause significant morbidity. Clinicians should consider patient risk factors (e.g., Given the potential risk of diabetic foot ulcers becoming infected, it is imperative to have a strong understanding of the current antibiotic options. These authors review 10 common antibiotics,
Abstract and Figures Aims: To develop an antibiotic foot formulary for the empirical treatment of diabetes-related foot infections presenting to our service.
Abstract Diabetic foot infection (DFI) management requires complex multidisciplinary care pathways with off-loading, debridement and targeted
Diabetes-related foot infections (DFIs) are one of the leading causes of hospitalization in people with diabetes. 1 Outcomes with DFIs can range from successful Only use antibiotics if clinical signs of infection Send microbiological samples early in infection – tissue aspirates are preferable to wound swabs Continue therapy until the INTRODUCTION Management of diabetic foot infections is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Treatment varies based on whether the infection is confined to soft

The prevalence of diabetes continues to increase globally and the International Diabetes Foundation has estimated that 537 million adults aged between 20 and 79 years worldwide
Foot infection is a well recognized risk factor for major amputation in diabetic patients. The osteomyelitis is one of the most common expression of diabetic foot infection, being present The committee agreed with the recommendation from the NICE guideline on diabetic foot problems, that antibiotics should be started as soon as possible for people with a suspected Background Diabetes-related foot infections are common and represent a significant clinical challenge. There are scant data about outcomes from large cohorts. The purpose of
The optimal duration of antibiotic therapy for soft-tissue infections of the diabetic foot remains unknown.We determine if antibiotic therapy after debridement for a short (10 Learn about the connection between cellulitis and diabetes, including risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options. Find out how diabetes affects the immune system and
The authors, on behalf of the Scottish Diabetes Group and the Scottish Infectious Diseases Society, provide broad, practical guidance on the use of antibiotics in people with diabetic foot
For specific information concerning the evaluation and management of diabetic foot infections, including choices of antimicrobial agents, the reader is referred to authoritative Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) stands as the foremost risk factor for infected foot ulcers, contributing to a myriad of chronic complications including cardiovascular, renal, Continuing Education Activity Diabetic foot infections are a major complication of diabetes mellitus and a leading cause of lower extremity amputations. This continuing
Background: The optimal antimicrobial treatment duration for diabetes-related foot osteomyelitis (DFO) currently needs to be determined. We systematically reviewed the effects of short and
Abstract The International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) has published evidence-based guidelines on the management and prevention of diabetes-related
Diabetic foot infections (DFIs) are a common complication of diabetes; however, there is clinical uncertainty regarding the optimal antimicrobial selection. The aim of this review The authors, on behalf of the Scottish Diabetes Group and the Scottish Infectious Diseases Society, provide broad, practical guidance on the use of antibiotics in people with Extended periods of broad-spectrum antibiotic regimens can contribute to antibiotic resistance and ultimately limit future treatment options. Furthermore, patient specific risk
- Anschluss Zu Delonghi Thermoblock
- Anthony William: Die Medical Medium 28 Tage Reinigung
- Antibell Hundehalsband Vibration
- Antworten Zu Psychischen Problemen Bei Kindern
- Antena Radio Novi Sad Uživo – Radio stanice Srbije uživo
- Ansichtskarte Aachen Restaurant Postwagen 1985
- Antiker Kulissentisch Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Anträge: Kommunalpolitisches Forum Nrw E.V.
- Antrag Auf Kostenerstattung Für Eine Familienheimfahrt
- Antonym Of The Word ‚Torpid‘ Is-
- Anschriften Und Kontaktmöglichkeiten
- Anti-Düz Kas Antikor Testi , Romatoloji Dahiliye Testleri
- Antike: Griechen Und Römer-Karteikarten
- Antalis: Neue Tools Für Eine Umweltbewusste Papierwahl