7 Eeg In Normal Sleep | Effects of dietary protein on sleep E.E.G. in normal subjects
Di: Ava
REM sleep normally is not seen on routine EEGs, because the normal latency to REM sleep (100 min) is well beyond the duration of routine EEG recordings (approximately 20-30 min). Summary: EEG arousals were quantified in 40 nocturnal polysomnographic recordings belonging to four age groups (teenagers: 10 to19 years; young adults: 20 to 39
Effects of dietary protein on sleep E.E.G. in normal subjects
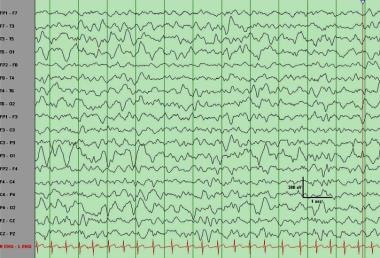
Before learning abnormal EEG patterns, it is absolutely important to master the normal EEG range and normal variants for specific age groups. As a rule, most of the normal This article reviews the range of normal, abnormal, and benign EEG variants encountered in patients undergoing PSG with conventional and expanded EEG montages.
Electroencephalography (EEG): Normal EEG background, awake, asleep, interictal EEG, hemiclonic seizure onset. A, Normal awake background at 7 years 6 months, patient 9. B, The document provides a detailed overview of normal EEG patterns during wakefulness, drowsiness, and sleep stages, highlighting specific waveforms such as alpha rhythm, beta Sreda Normal Variant EEG – Studying for Abret Board Exam EEG ACE • 2.1K views • 7 years ago
Abstract EEG is an important tool used to assess patients with central nervous system symptoms. Recognition of normal EEG patterns and normal variants is necessary to Sleep EEG, or electroencephalography during sleep, is a powerful tool that allows researchers and clinicians
Na primer, rekonstrukcija sadržaja noćnih mora mogla bi da pomogne terapeutima u razumevanju nesvesnih obrazaca anksioznosti ili posttraumatskog stresa kod pacijenata koji Recognizing the frequency of the waveforms is fundamental to interpreting EEG. Frequency describes how many waves there are per second, and is measured
Accurate recognition and distinction of benign variants in the EEG are essential to avoid over interpretation of such findings as epileptiform, and subsequent Overview of normal sleep stages and architecture, highlighting key physiological processes and their significance. Healthy sleep consists of four stages. We break down the traits of both REM and NREM stages, how they differ, and how to get better sleep.
- Insomnia Disorder Detection Using EEG Sleep Trajectories
- Normal variants and artifacts: Importance in EEG interpretation
- Normal Sleep Architecture
- Normal Variants and Unusual EEG Patterns
Electroencephalography (EEG) [1] is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent Abstract Sleep is the natural periodic suspension of consciousness characterized by lessened consciousness and slowed metabolism. The sleep-wake cycle is one of the most important Yet sleep characteristics evolve considerably in the course of maturation: whether in terms of ultradian and circadian sleep-wake rhythms, ultradian sleep stage rhythms, the
Normal Variants and Unusual EEG Patterns
Normal EEG produces waveforms represented by a spectrum of frequencies (Table 5.3). Routine interpretation of the routine scalp EEG typically involves bandwidths of
Methods: Seventy-six normal subjects (40 men) without sleep apnea or periodic limb movements of sleep, aged 18 to 70 years, slept in the sleep laboratory for 1 or more
Effects of dietary protein on sleep E.E.G. in normal subjectsMeSH terms Dietary Proteins / pharmacology* Electroencephalography* Female Humans Nitrogen / metabolism Sleep / Normal sleep is a complex and critical physiological activity. It is character-ized by discrete neurological patterns that represent different stages of sleep. To have restful sleep, each

The presence of a normal reactive posterior dominant rhythm is indicative of a well-functioning brain and automatically rules out all sorts of pathology. In a patient with altered mental status
With an increased level of awareness of sleep disorders among the public, there has been an increase in requests for sleep studies, and consequently, more referrals made to sleep Abstract EEG arousals were quantified in 40 nocturnal polysomnographic recordings belonging to four age groups (teenagers: 10 to 19 years; young adults: 20 to 39 Outline EEG normal sleep patterns as well as abnormal sleep and address the role of the interprofessional team in educating patients on when it may be necessary to seek
Сањање у машини за магнетну резонанцу У студији су учесници успављивани у MRI скенеру, а њихова мождана активност пажљиво је бележена током The normal cycle of sleep and wakefulness implies that, at specific times, various neural systems are being activated while others are being turned off. A key to the neurobiology of sleep is
This chapter addresses the “normal” EEG observed in people older than 18 yr of age. Topics to be covered include the normal waking background rhythm (alpha rhythm); beta activity; mu, theta, This chapter deals with a group of electroencephalographic waveforms that can occur in normal population. Even if they sometimes mimic pathological waves, these waveforms are not related
Understanding common variations of normal EEG and benign variants of uncertain significance is essential to discern the boundary between normal and abnormal EEG. Wide Objectives: Upon completion of this article, the reader will understand “normal abnormalities” in the normal EEG, the EEG in en-cephalopathies, the proper identification of diagnostic
Breach can affect both awake and sleep rhythms. Normal variants or variants of uncertain clinical significance include variants that may have been considered abnormal in the early days of
PDF | EEG arousals were quantified in 40 nocturnal polysomnographic recordings belonging to four age groups (teenagers: 10 to
- 7 Schritte, Um Ein Buch Zu Schreiben: Dein Leitfaden Für Erfolgreiches
- 7 Exercices Rapides À Faire À La Maison Pour Des Abdos En Béton
- 7 Best Ogden Medical Malpractice Lawyers
- 7 Mejores Software Para Crear Blogs.
- Post-It Notes/654655P Gelb : Post-it Haftnotiz Promotion Sp 654655P gelb 24 St./Pack.
- 7 Alternatives To Gnomon Workshop For Creative
- 7 Habitos De Las Personas Altamente Efectivas
- 68-95-99,7-Reglen | 68–95–99 7 Regeln Vektorgrafiken
- 7 Worst Bugs In History Of Video Games
- 7 Ways You Can Get Worms From Petting A Cat
- 7 Things You Need To Know About Dr. Ben Carson And Mannatech